Exploring the Fascinating Realm of Threatened and Endangered Wildlife


Evergreen Trees Species
Evergreen trees are a vital component of American forests, providing not only aesthetic beauty but also crucial ecological functions. In this section, we will delve into the diverse array of evergreen tree species that populate these forests, from the majestic Douglas fir to the resilient redwoods and pines. Understanding the unique characteristics of each species is essential to appreciating the biodiversity and intricate ecosystems that rely on these iconic trees.
Types of Evergreen Trees Explore the vast tapestry of evergreen tree species that grace American forests, including the iconic sequoias of the Pacific Northwest, the aromatic cedars of the Appalachian Mountains, and the stately spruces of the Great Lakes region. Each species has adapted uniquely to its environment, exhibiting a remarkable resilience to a variety of climatic conditions and ecological niches.
Ecological Significance The ecological significance of evergreen trees cannot be overstated. These majestic trees serve as crucial carbon sinks, sequestering large amounts of carbon dioxide and helping mitigate the impacts of climate change. Additionally, they provide habitat and sustenance for a diverse array of wildlife, from the nesting sites of birds to the shelter for small mammals and insects. Understanding the interconnectedness of these ecosystems is key to preserving their delicate balance.
Conservation Practices Preserving evergreen tree species requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses not just protection from logging and deforestation but also active restoration efforts. Implementing sustainable forestry practices, such as selective logging and reforestation initiatives, can help ensure the long-term viability of these valuable ecosystems. By employing cutting-edge conservation methods backed by scientific research, we can safeguard the future of these iconic trees for generations to come.
Introduction
In the vast realm of biodiversity, the designation of species as threatened or endangered carries immense significance. This introductory section serves as the gateway to understanding the gravity of the situation faced by various flora and fauna. By addressing the nuances of endangered species, we begin to unravel the intricate tapestry of challenges and solutions intertwined with wildlife conservation efforts. Delving into the foundations of categorization and protection, the introduction sets the stage for an enlightening exploration of the Threatened and Endangered Species List.
Defining Endangered Species
The IUCN Red List Criteria
The IUCN Red List Criteria stands as a beacon of evaluation for species at risk, laying down stringent parameters for assessing their conservation status. This methodical approach considers factors such as population size, habitat vulnerability, and rate of decline to categorize species under varying levels of endangerment. Its systematic framework not only ensures scientific rigor but also enables a global standard for monitoring and safeguarding threatened biodiversity. While the adherence to these criteria may present challenges in certain contexts, its holistic nature fosters comprehensive conservation strategies vital for protecting vulnerable species.
Categorical Classification of Threats
Moving beyond assessment, the Categorical Classification of Threats broadens our perspective by identifying the diverse range of risks faced by wildlife populations. Through categories encompassing habitat loss, climate change impact, and human exploitation, this classification scheme highlights the multifaceted nature of endangerment factors. By delineating these threats into distinct groups, conservation efforts can be tailored to address specific vulnerabilities effectively. However, the flexibility within these categories might also introduce complexities in prioritizing conservation actions, necessitating a nuanced approach to mitigate concurrent risks and ensure long-term species protection.
Causes of Species Endangerment
In this section of the article, we delve into the critical topic of Causes of Species Endangerment, shedding light on the fundamental factors that contribute to the vulnerability of various species. Understanding the root causes of endangerment is paramount in devising effective conservation strategies to safeguard biodiversity. By exploring the intricate web of interactions between human activities and environmental changes, we aim to highlight the pressing need for proactive measures to mitigate species decline and promote sustainable coexistence.
Habitat Destruction
Deforestation
The rampant practice of Deforestation stands out as a key driver behind species endangerment. This systematic removal of forests for commercial purposes not only diminishes vital habitats for countless flora and fauna but also disrupts ecological balance on a global scale. The accelerated pace of deforestation, driven by demands for timber, agricultural expansion, and urban development, has led to irreversible losses in biodiversity. This section provides a detailed analysis of the impacts of deforestation on endangered species, emphasizing the urgent conservation actions required to curb this destructive trend.

Urbanization Impact
The burgeoning phenomenon of Urbanization Impact exerts immense pressure on natural ecosystems, resulting in habitat fragmentation and degradation. As urban centers expand, wildlife habitats are increasingly encroached upon, leading to heightened competition for resources and heightened susceptibility to human-wildlife conflicts. Furthermore, urbanization contributes to pollution, habitat destruction, and the introduction of invasive species, posing significant threats to vulnerable species. Examining the implications of urbanization on biodiversity conservation is crucial for devising sustainable urban planning strategies that balance human needs with wildlife preservation.
Climate Change
Impact on Biodiversity
The far-reaching consequences of Climate Change on biodiversity are becoming increasingly evident, with shifts in temperature patterns, altered precipitation regimes, and extreme weather events wreaking havoc on fragile ecosystems. The impact of these changes on biodiversity manifests in the form of altered species distributions, disrupted food webs, and increased susceptibility to diseases. By elucidating the interconnectedness between climate change and species endangerment, we aim to underscore the urgent need for climate mitigation and adaptation measures to protect biodiversity.
Rising Temperature Effects
The escalating trends of Rising Temperature Effects pose significant challenges to biodiversity conservation efforts worldwide. As temperatures soar, ecosystems face heightened risks of desertification, habitat loss, and species extinctions. The cascading effects of rising temperatures reverberate through ecosystems, affecting species interactions, migration patterns, and reproductive success. Analyzing the specific implications of rising temperatures on biodiversity provides valuable insights into the strategies needed to mitigate climate-related threats and ensure the resilience of ecosystems.
Poaching and Illegal Trade
Trafficking Networks
The nefarious activities of Trafficking Networks pose a severe threat to endangered wildlife populations, driving many species to the brink of extinction for monetary gains. These intricate networks operate globally, exploiting legal loopholes and lax enforcement measures to engage in the illicit trade of endangered species and their products. By exposing the inner workings of trafficking networks and highlighting their detrimental impacts on biodiversity, we aim to enhance awareness and empower concerted efforts to combat wildlife crime.
Endangered Species Markets
The proliferation of Endangered Species Markets perpetuates the demand for rare and exotic species, driving unsustainable exploitation of wildlife for luxury goods, traditional medicines, and status symbols. These markets fuel the illegal trade in wildlife products, exacerbating the decline of already imperiled species. Exploring the dynamics of endangered species markets sheds light on the complexities of demand-driven biodiversity loss and underscores the urgency of regulatory interventions and consumer awareness campaigns to curb the trade in endangered species.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts play a pivotal role in safeguarding the delicate balance of our ecosystem. In the context of this insightful exploration of the threatened and endangered species list, delving into the realm of conservation efforts unveils a multifaceted approach towards protecting and preserving biodiversity. By emphasizing the significance of conservation efforts, this section aims to shed light on the proactive measures required to mitigate the looming threats faced by endangered wildlife. Conservation efforts encompass a myriad of strategies ranging from on-ground conservation actions to policy advocacy and community engagement. By focusing on specific elements such as habitat restoration, species reintroduction programs, and sustainable resource management, this article elucidates the holistic approach required to combat species endangerment. The benefits of conservation efforts extend beyond protecting individual species; they contribute to the overall health of ecosystems, foster biodiversity conservation, and ensure sustainable development practices for present and future generations.
Protected Areas and Reserves
National Parks
National Parks epitomize the essence of conservation efforts by providing protected spaces for a diverse array of flora and fauna. Their contribution to biodiversity conservation is unparalleled, offering a safe haven for endangered species to thrive in their natural habitats. The key characteristic of National Parks lies in their ability to conserve unique ecosystems, critical habitats, and iconic species. They stand out as beneficial choices for this article due to their well-established conservation frameworks, stringent protection measures, and scientific research opportunities. One unique feature of National Parks is their role in promoting ecotourism, which generates revenue for conservation initiatives while raising public awareness about the importance of preserving natural landscapes. Despite their advantages, challenges such as managing visitor impact, combating illegal activities, and securing adequate funding remain prevalent.


Wildlife Sanctuaries
Wildlife Sanctuaries serve as designated areas specifically managed to protect wildlife species and their habitats. Their contribution to the overall goal of biodiversity conservation is instrumental, providing refuges for species under threat and functioning as vital breeding grounds for wildlife populations. The key characteristic of Wildlife Sanctuaries is their emphasis on specific species conservation, enabling targeted efforts towards the protection of endangered or vulnerable wildlife. They are popular choices for this article due to their direct focus on wildlife protection, habitat restoration, and research facilitation. A unique feature of Wildlife Sanctuaries is their role in fostering scientific research and monitoring programs that contribute valuable data for species conservation and ecosystem management. While Wildlife Sanctuaries offer significant advantages in wildlife protection and research, challenges such as habitat fragmentation, human-wildlife conflicts, and limited resources pose ongoing difficulties in their effective management.
Legislative Measures
The effectiveness of conservation efforts heavily relies on robust legislative measures that provide a legal framework for protecting endangered species and their habitats. In the context of this article, exploring legislative measures unveils the critical role that policy and regulations play in shaping conservation outcomes. The specific aspect of the Endangered Species Act exemplifies a cornerstone in conservation legislation by offering protection to species at risk of extinction and their critical habitats. Its key characteristic lies in the legal mandate to identify and recover endangered species, preventing their extinction and promoting population restoration. The Endangered Species Act is a beneficial choice for this article due to its comprehensive approach to species conservation, mandated recovery plans, and enforcement mechanisms. A unique feature of the Endangered Species Act is its provision for critical habitat designation, ensuring the preservation of essential habitats for species survival. Despite its advantages in species protection and recovery, challenges such as funding constraints, political opposition, and regulatory complexities pose obstacles to its full implementation.
International Agreements
International Agreements serve as global platforms for countries to collaborate on conservation initiatives and address transboundary environmental challenges. Their contribution to the overall goal of biodiversity conservation is paramount, fostering international cooperation, data sharing, and collective action towards environmental protection. The key characteristic of International Agreements lies in harmonizing conservation efforts across nations, promoting sustainable practices, and sharing best practices for species conservation. They are beneficial choices for this article due to their role in facilitating cross-border conservation projects, promoting scientific exchange, and standardizing conservation protocols. A unique feature of International Agreements is their capacity to influence policy at a global scale, setting conservation targets, and establishing monitoring mechanisms for species protection. Despite their advantages in promoting international cooperation and biodiversity conservation, challenges such as political differences, limited enforcement mechanisms, and diverse stakeholder interests impede the effective implementation of international agreements.
Community Engagement
Community Engagement forms the cornerstone of successful conservation efforts by involving local communities in decision-making processes, raising awareness about conservation issues, and fostering a sense of stewardship towards the environment. In the context of this article, exploring community engagement unveils the pivotal role that communities play in shaping conservation outcomes and ensuring the sustainability of conservation initiatives at the grassroots level. The specific aspect of Education Initiatives highlights the importance of educational programs in building conservation awareness, developing environmental literacy, and empowering communities to become conservation advocates. The key characteristic of Education Initiatives lies in their capacity to bridge the gap between scientific knowledge and public understanding, fostering a culture of conservation ethics and responsible environmental stewardship. Education Initiatives are beneficial choices for this article due to their role in promoting environmental education, fostering public engagement, and empowering individuals to make informed decisions about conservation practices. A unique feature of Education Initiatives is their potential to cultivate a new generation of environmental leaders, conservationists, and advocates who drive positive change in conservation efforts. Despite their advantages in raising conservation awareness and promoting behavior change, challenges such as limited resources, insufficient training, and competing priorities hinder the effectiveness of education initiatives in achieving long-term conservation goals.
Local Participation
Local Participation amplifies the impact of conservation efforts by involving local communities in conservation planning, resource management, and decision-making processes. Its contribution to the overall goal of biodiversity conservation is crucial, as local communities possess invaluable traditional knowledge, expertise, and insights into local environments. The key characteristic of Local Participation lies in fostering community ownership, building collaborative partnerships, and promoting sustainable resource use practices. It is a beneficial choice for this article due to its emphasis on community-based conservation strategies, empowering local stakeholders, and integrating traditional ecological knowledge into conservation programs. One unique feature of Local Participation is its ability to foster socio-economic development, sustainable livelihoods, and cultural preservation within local communities. Despite its advantages in promoting community stewardship and resource management, challenges such as power imbalances, conflicting interests, and lack of inclusivity pose barriers to meaningful local participation in conservation efforts.
Impact of Human Activities
The topic of Impact of Human Activities plays a crucial role in this article by shedding light on the significant influence of human actions on the endangerment of species. Human activities such as urban development have led to widespread negative impacts on wildlife and ecosystems, making it imperative to delve deeper into this subject. Understanding the implications of human actions is vital for formulating effective conservation strategies and mitigating the threats faced by endangered species.
Urban Development
Infrastructure Expansion
In the context of this article, Infrastructure Expansion emerges as a key element contributing to the degradation of natural habitats and the decline of vulnerable species. The relentless push for urban infrastructure projects not only encroaches upon crucial wildlife corridors but also disrupts ecological balance. The rapid growth of infrastructure, including roads, buildings, and industrial facilities, exerts immense pressure on ecosystems, leading to habitat fragmentation and loss.
Furthermore, the distinctive feature of Infrastructure Expansion lies in its ability to facilitate human expansion at the expense of biodiversity. While infrastructure development is often seen as a sign of progress and economic growth, its implications for wildlife are often overlooked. Despite the perceived benefits of infrastructure expansion, such as improved connectivity and urban amenities, its adverse effects on wildlife populations and their habitats cannot be ignored.
Agricultural Encroachment


Another aspect of human activities, Agricultural Encroachment, significantly contributes to the overarching theme of species endangerment explored in this article. The conversion of natural landscapes into agricultural land poses a severe threat to biodiversity, leading to habitat destruction and species loss. The expansion of agricultural activities not only diminishes available habitats for wildlife but also results in increased conflicts between humans and animals.
The key characteristic of Agricultural Encroachment lies in its pervasive nature, as agriculture is a fundamental component of human survival and livelihood. However, the intensive nature of modern agricultural practices, such as monoculture and pesticide use, often leads to ecological imbalances and negative repercussions for biodiversity. While agriculture is essential for food production and economic sustenance, it is essential to address the environmental repercussions of unchecked agricultural expansion.
Moreover, Agricultural Encroachment brings forth a unique set of challenges and opportunities for conservation efforts. Balancing the need for agricultural productivity with wildlife conservation requires innovative solutions and sustainable practices. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of agricultural encroachment in the context of species endangerment, stakeholders can work towards harmonizing human activities with biodiversity conservation.
Case Studies
Endangered Species Examples
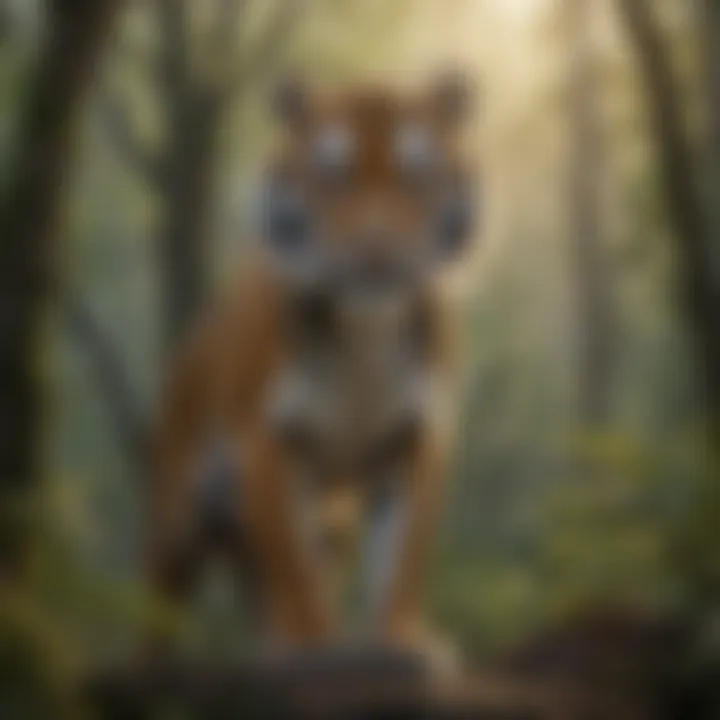
Sumatran Tiger
The Sumatran Tiger stands as a poignant representation of endangered species in the context of this exploration. Renowned for its distinctive striped coat and elusive nature, the Sumatran Tiger embodies the struggles many species face due to habitat loss and poaching. Its unique feature lies in being the last tiger subspecies native to Indonesia, facing severe threats from rampant deforestation and illegal wildlife trade. By focusing on the Sumatran Tiger, we shed light on the dire consequences of human encroachment on natural habitats, underscoring the urgency of conservation efforts in safeguarding this iconic species.
California Condor
Conversely, the California Condor offers a compelling case study in avian conservation. Known for its expansive wingspan and endangered status, the California Condor symbolizes the challenges of reestablishing populations on the brink of extinction. Its key characteristic lies in being one of the largest flying birds in North America, facing population decline primarily due to lead poisoning and habitat destruction. With concerted conservation efforts and captive breeding programs, the California Condor exemplifies the resilience of species when supported through strategic conservation initiatives. By examining its plight, we gain insight into the delicate balance between humanity's actions and wildlife preservation.
Future Outlook
As we delve into the future outlook of endangered species, it becomes imperative to emphasize the critical importance of long-term sustainability and conservation strategies in safeguarding vulnerable wildlife populations. This section of the article aims to shed light on the forward-thinking approaches and initiatives that are pivotal in shaping the future landscape of biodiversity conservation.
Looking ahead, sustainable conservation strategies emerge as the cornerstone of preserving fragile ecosystems and safeguarding endangered species from further decline. By implementing practices that prioritize the long-term health of ecosystems and the species they support, conservation efforts can significantly impact the trajectory of threatened wildlife populations.
Challenges Ahead
Sustainable Conservation Strategies
Delving deeper into sustainable conservation strategies, it is essential to underscore their role in fostering resilient ecosystems and ensuring the survival of endangered species. The specific aspect of sustainable conservation strategies lies in their ability to promote biodiversity conservation through ecologically sound practices.
One key characteristic of sustainable conservation strategies is their focus on balancing the needs of human society with nature's intricate ecosystems. This balance ensures that conservation efforts are not only effective but also sustainable in the long run, benefiting both wildlife and communities alike.
A unique feature of sustainable conservation strategies is their emphasis on adaptive management techniques, allowing conservationists to adjust their approach based on evolving environmental dynamics. While these strategies offer numerous advantages, such as promoting biodiversity and ecosystem services, they also come with challenges such as the need for continuous monitoring and adaptation to changing ecological conditions.
Public Awareness Initiatives
In addressing the challenges ahead, public awareness initiatives play a crucial role in amplifying the impact of conservation efforts. These initiatives focus on engaging and educating the public on the significance of biodiversity conservation and the importance of protecting endangered species.
The key characteristic of public awareness initiatives is their ability to mobilize communities and individuals towards collective action in preserving ecosystems and wildlife. By raising awareness about the importance of conservation, these initiatives foster a sense of responsibility and stewardship towards the environment.
A unique feature of public awareness initiatives is their capacity to drive policy changes, influence consumer behavior, and cultivate a culture of conservation consciousness. While they have proven to be effective in mobilizing public support, challenges such as maintaining long-term engagement and addressing diverse stakeholder interests need to be navigated for sustained impact.



