Post-Tick Actions: Essential Steps for Safety

Intro
Finding a tick on your body can throw anyone into a tailspin. It’s a moment of panic, worry about what that little creature could mean for your health. Knowing what to do afterwards is crucial. This guide intends to untangle the important steps to take after discovering a tick. From identification to removal, and from post-extraction care to mindful monitoring for potential tick-borne diseases, everything is encompassed in this narrative.
As we dig into these aspects, the discussion will unveil underlying themes about wildlife interactions and forest health. It becomes not just about a singular encounter, but the broader ecosystem that weaves through our environment and impacts our lives. By the time you finish reading, you'll have a stronger grasp of how to navigate this unsettling experience,
Types of Ticks
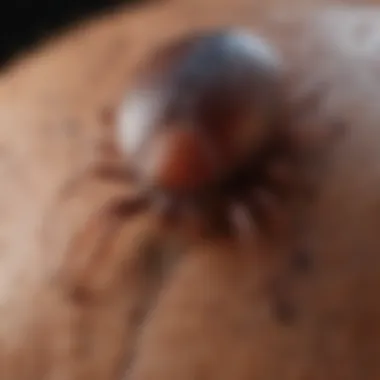
Understanding the kind of tick you’re dealing with is the starting point. Common types like the black-legged tick, often known as the deer tick, and the dog tick can carry various diseases. Each breed has its quirks; the deer tick is smaller, making it more elusive, while the dog tick is easier to spot.
Safe Removal Techniques
Once identified, it’s time for removal. Using fine-tipped tweezers is the gold standard. Grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pull upwards with steady, even pressure. Twisting might leave parts behind, and that’s not what you want.
Post-Extraction Care
After removing the tick, it’s vital to clean the bite area with soap and water. An antiseptic or rubbing alcohol could provide added protection against infection. Keeping an eye on the site for any unusual symptoms is crucial. If you notice a rash or fever, it's time to consult a healthcare professional.
“A watchful eye can be your best friend after a tick discovery.”
Monitoring for Tick-Borne Diseases
Tick-borne diseases can be tricky. Lyme disease often presents itself as a bull’s-eye rash. However, not everyone gets that telltale sign. Therefore, knowing the symptoms is key. Keep a log of any physical changes you feel in the weeks following the tick removal, particularly if further complications arise.
Importance of Preventive Measures
Prevention certainly beats cure. Understanding habitats, using repellents, and wearing appropriate clothing can significantly reduce your chances of tick encounters. The more prepared you are, the lesser the odds you’ll find yourself staring down a tick.
Closure
Navigating a tick encounter doesn’t have to be a disorganized scramble. With this guide, you have ready-access tips and strategies to tackle the situation with confidence. In the future, understanding ticks can contribute not only to personal well-being but also to fostering a healthier relationship with our ecosystems.
Understanding Ticks
Ticks are small arachnids that carry significant implications for health and wellbeing, particularly in relation to the diseases they can transmit. Understanding ticks forms the backbone of this guide, as it enables individuals to recognize the risks associated with a tick encounter and respond appropriately. This section delves into the diverse types of ticks, their habitats, and lifecycle, providing a framework for effective post-tick discovery actions.
Types of Ticks
Deer Ticks
Deer ticks, also known as black-legged ticks, are infamous for their role in transmitting Lyme disease. They prefer wooded and brushy areas where they can easily latch onto hosts like deer, which plays a critical part in their life cycle. The key characteristic of deer ticks is their small size, particularly in the larval stage, which can make them hard to spot. This aspect is particularly crucial for the article since it emphasizes the need for vigilance when in tick-prone areas.
One unique feature of deer ticks is their color changing ability; they often become darker after a blood meal, which might help with identification post-encounter. However, their resemblance to other tick varieties can pose identification challenges.
Wood Ticks
Wood ticks, or American dog ticks, tend to be larger than deer ticks and are frequently found in grassy areas. Their presence is an important consideration for outdoor enthusiasts, as they hunt for hosts in open spaces. The prominence of wood ticks in this guide stems from their capacity to transmit diseases like Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever.
A key element contributing to their significance is their lifecycle pattern, which allows them to thrive in various environments. This adaptability to different habitats makes awareness of wood ticks essential, highlighting the importance of protective measures, especially during warmer months.
Brown Dog Ticks
In contrast to the former two, brown dog ticks primarily live in close association with dogs and often infest indoor spaces. Their ability to thrive indoors is a unique aspect that sharply distinguishes them from other tick species. Brown dog ticks can transmit illnesses such as canine Ehrlichiosis, which can complicate the dynamics of tick-borne diseases in both pets and humans.
The main characteristic contributing to their profile in this article is their tendency to be found in urban settings, making it crucial for pet owners to be mindful. Being aware of brown dog ticks and their habitat increases one's ability to take preventive measures and maintain good health.
Tick Habitats
Forest Environments
Forest environments are a natural habitat for ticks, offering the dense cover they thrive in. Such regions provide ample opportunities for ticks to attach to passing animals or humans. This section holds great weight within the article as it emphasizes the risk factors present in natural settings.
Key traits of forest environments include the variety of host animals available for ticks, which forms the basis of their lifecycle and reproduction. Understanding these characteristics can help individuals strategize when traversing forested lands, knowing to wear protective clothing and use insect repellent.
Grasslands
Grasslands are another significant habitat for ticks. They often appear in open fields and meadows, making it easier for ticks to latch onto unsuspecting individuals. This characteristic is integral to the article, as many outdoor activities take place in such settings, increasing exposure risks.
The challenge with grasslands is their abundant growth, providing both cover for ticks and access to host animals. Engagement in activities like hiking or picnicking in these areas necessitates increased caution and awareness.
Urban Areas
Ticks are not restricted to rural environments; urban areas also host ticks, particularly certain species like the brown dog tick. This surprising fact sheds light on the potential risks posed by ticks in cities where pets might roam freely.
Highlights from urban habitats include the presence of parks and gardens where ticks can proliferate in warmer months. This makes knowledge of their existence in these spaces essential for residents and pet owners alike, ensuring a proactive approach to risk management.
Ticks and Their Lifecycle
Lifecycle Stages
Understanding the lifecycle stages of ticks is pivotal, imparting comprehension of their breeding patterns, which can facilitate prevention strategies. Ticks undergo four life stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. The time spent in each stage varies, with adults often thriving during specific seasons, generally favoring warm, humid conditions.
This knowledge instructs individuals on when ticks are most active and poses greater risks of encountering them. Recognizing the lifecycle aids in understanding the connection between tick behavior and applicable prevention techniques.
Feeding Patterns
Feeding patterns of ticks significantly affect their lifecycle and the transmission of diseases. Ticks typically wait on vegetation, ready to attach themselves to passing hosts. They prefer larger hosts as they typically provide sufficient blood meals required for maturation.
The emphasis on feeding patterns is important in this article as it underscores when individuals are most at risk. Knowing these habits can shape practices geared towards avoiding tick bites, such as using tick repellents or sticking to cleared paths.
Seasonal Activity
Ticks exhibit variation in seasonal activity, generally becoming more prominent during the spring and fall months. Their populations surge with ecological conditions that favor survival and reproduction. This point is particularly relevant for those indulging in seasonal outdoor activities, as awareness during peak tick seasons can guide preventive measures.
Recognizing the regular patterns of ticks aids in encouraging proactive behavior, such as scheduling outdoor explorations during times when tick activity is lower.
Immediate Actions After Finding a Tick
Discovering a tick on your body can stir up a flurry of emotions, from anxiety to confusion. It's essential to respond swiftly and effectively to minimize any potential health risks. This section highlights the urgency of immediate actions and outlines the steps necessary to address the situation competently.
Identifying the Tick
Visual Inspection


Conducting a thorough visual inspection should be your first move upon discovering a tick. This process involves closely examining the tick's characteristics, such as its size, color, and shape. Ticks can vary significantly among species, and the diagnostic feature can play a crucial role in determining the potential risks associated with that particular tick. For example, Lyme disease is prominently linked to deer ticks, while brown dog ticks are often carriers of other diseases.
The key characteristic of visual inspection is its immediacy; you can do it right where you are without needing additional tools. This method is beneficial as it helps identify the type of tick and estimate how long it has been attached, which is key for assessing disease transmission risk. However, some ticks can be difficult to distinguish from one another.
Resources for Identification
Utilizing various resources for identification can significantly enhance your understanding of the tick you’ve encountered. Online platforms, field guides, or local health department resources can provide visual references that facilitate accurate identification of different tick species. Moreover, various community health organizations often offer educational material or services to assist in identifying ticks.
The key characteristic of these resources is their accessibility. Many provide up-to-date information and images that make identification more straightforward. They remain a popular choice, particularly for individuals who may not have prior experience dealing with ticks. An advantage of these resources is their breadth; they usually cover multiple tick species and can inform you of geographical differences as well. On the downside, the information can sometimes be overwhelming or too technical for someone looking for quick help.
Differences between Species
Understanding the differences between tick species is crucial for gauging health risks. Each species harbors varying disease potentials and behaviors; not all ticks are dangerous. For instance, while deer ticks are notorious for Lyme disease, others, such as the lone star tick, can also transmit other diseases like ehrlichiosis but often go unnoticed until symptoms surface.
The key characteristic here lies in the recognition of unique features—such as the shape of their mouthparts, size, and coloration. This knowledge is particularly valuable when assessing risks and planning appropriate actions. However, the downside is that many people are unfamiliar with tick anatomy, which can lead to confusion and misidentification.
Proper Removal Techniques
Using Fine-Tipped Tweezers
Using fine-tipped tweezers is widely regarded as one of the most effective methods for tick removal. The technique requires grasping the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pulling upward with steady, even pressure. This method minimizes the chances of leaving tick parts lodged in the skin, which could lead to infections.
A key characteristic of using tweezers is precision; fine-tipped tweezers allow you to grip the tick firmly without crushing it. This beneficial approach minimizes the risk of introducing pathogens into the bloodstream. However, using an improper tool, like fingers, may result in incomplete removal or even squeezing the tick’s body, which can release harmful substances into your bloodstream.
Methods to Avoid
While some approaches may sound tempting, it's crucial to avoid certain methods that have been proven ineffective or dangerous. Techniques such as burning the tick with a match, applying petroleum jelly, or using alcohol can cause the tick to regurgitate its contents into the wound, increasing the likelihood of infection.
A key characteristic of these methods is their reliance on untested home remedies that can actually worsen health outcomes in those bitten by ticks. They are commonly mentioned but should not be tried as they lead to more complications. Recognizing these methods can save you from further health problems.
Post-Removal Care
After successfully removing the tick, the focus should shift to post-removal care. This encompasses cleansing the bite area vigorously with soap and water and possibly applying an antiseptic to prevent any secondary infections. It’s also recommended to keep a close watch for any signs of a tick-borne illness, which might emerge days or even weeks after the encounter.
The key characteristic of post-removal care is its critical role in ensuring a complete recovery. This crucial step is not merely about removing the tick; it’s also about safeguarding your health after the fact. However, neglecting proper care can lead to complications, so being diligent in this aspect is paramount.
"Always err on the side of caution; if uncertain, consult a healthcare provider for advice post-tick removal."
By addressing these vital steps, individuals can better manage the immediate aftermath of finding a tick and develop a more informed approach to their health. Understanding what actions to take is key in the fight against tick-borne diseases and can contribute to improved outcomes.
Post-Removal Considerations
After removing a tick, there is more to think about than just getting it off your skin. Post-removal considerations play a vital role in ensuring your health and understanding your body’s reaction. It’s crucial to be attentive and monitor for symptoms that may arise as well as document the encounter for future reference. This section lays out the necessary actions to take following the tick removal, ensuring a proactive approach toward your wellbeing.
Monitoring for Symptoms
Keeping an eye out for any abnormal symptoms after a tick encounter is an essential task. This process helps in timely detection of any diseases that could follow. Taking notes on your health can really make a big difference.
Signs of Infection
When assessing signs of infection, you should look out for redness, swelling, or warmth around the area where the tick was removed. These symptoms can indicate an inflammatory response or infection. The key characteristic is recognizing these signs early; this allows for swift action if additional care is needed. If you notice any of these symptoms developing, that's a signal to remain vigilant.
The unique feature of monitoring for signs of infection is your body’s natural responses. While minor irritation may happen to most people, significant redness or a rash could suggest an infection or even a tick-borne disease. Early identification can lead to earlier treatment, which can make a world of difference in your recovery.
Tick-Borne Diseases Overview
Understanding the broader picture of tick-borne diseases is vital. After removal, there’s a risk of transmitting these diseases depending on the tick's species and how long it was attached. Key diseases include Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever, which can manifest weeks after the initial tick encounter. This awareness is crucial.
The unique characteristic of this section is linking symptoms to specific tick-borne illnesses. It helps in connecting the dots between the encounter and what signs may indicate that you’re at risk. Each disease has its own set of symptoms and some may not appear right away, so ongoing awareness is important even weeks after the removal.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to reach out for medical help can save a lot of trouble. If symptoms become severe or if you develop a fever, joint pain, or a rash resembling a “bull's-eye,” it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. The key characteristic of this advice is the focus on recognizing warning signs that shouldn’t be ignored.
One unique aspect of knowing when to seek medical attention is the subjective perception of symptoms. People may hesitate to seek care, thinking symptoms are mild, but in tick-related cases, it's better to err on the side of caution. Therefore, seeking medical help as soon as something feels off is encouraged.
Documenting the Encounter


Documentation plays a significant role in post-tick discovery actions. It's not just a record; it's a way to track your health and provide precise information to healthcare providers if need be.
Recording Dates and Locations
Being methodical about noting when and where you found the tick can assist in identifying potential risk factors later on. The key characteristic here is thoroughness; noting the exact date and location can be critical when discussing symptoms with a doctor.
A unique feature of this task is its potential for establishing patterns. If multiple tick encounters occur in the same location, it may indicate a 'hot spot' of ticks and signal the need for more focused prevention measures in that area. This helps in building a complete picture of your exposure to ticks over time.
Photographic Evidence
Having a photographic record of the tick and the site of removal can bolster your case if you need to consult medical personnel later. Take clear images showing both the tick and your skin post-removal. The key characteristic of this method is clarity; it aids in explaining the situation should medical attention become necessary.
The unique aspect of using photographs is that visual evidence often speaks louder than words, providing immediate context. However, ensure images are detailed and clear; poor-quality photos may cause confusion rather than clarity.
Health Tracking
Tracking your health is a beneficial action following a tick encounter. Keeping a journal or using an app to document changes in your symptoms can highlight relevant information later. The key characteristic of health tracking is regular monitoring; it allows for a comprehensive view of how you feel over time.
A unique part of this engagement is the increased awareness you gain about your body. This proactive measure can enhance your understanding of what feels normal versus what is alarming, ultimately empowering you to take control of your health choices and decisions.
Keeping comprehensive records and monitoring responses isn’t just about being cautious; it can save your life if something goes sideways.
Understanding Tick-Borne Diseases
Understanding tick-borne diseases is critical for individuals who frequently encounter ticks, whether in a wooded area or even a backyard. This section emphasizes the necessity of recognizing these diseases and their potential health impacts. With a thorough grasp of what these illnesses entail, individuals can be more proactive in monitoring their health after a tick encounter. Awareness is not just a safeguard for oneself but also a pivotal part of broader public health discussions, particularly in areas where ticks are prevalent.
Common Tick-Borne Illnesses
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is perhaps the most well-known tick-borne illness. This disease stands out due to its prevalence and potential long-term effects on health. It is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, primarily transmitted through the bite of infected deer ticks. The distinctive skin rash, often resembling a target, is a hallmark sign of this condition. This specific characteristic makes it easier to identify, which in turn allows for prompt treatment and a better prognosis. Awareness of Lyme disease is essential as the illness can lead to serious complications if left untreated, sometimes affecting the joints, heart, or nervous system.
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Rocky Mountain spotted fever is another significant disease that deserves attention. Caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii, it is typically transmitted through the bite of infected American dog ticks. What sets this disease apart is the rapid onset of symptoms, which can include fever, rash, and severe headache. This swift manifestation makes it crucial for individuals to identify potential tick encounters quickly and seek medical attention accordingly. The recognition of the disease's aggressive nature reinforces the importance of understanding tick-borne illnesses — early diagnosis is key to reducing morbidity and mortality associated with this condition.
Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis is less widely recognized than Lyme disease or Rocky Mountain spotted fever but equally important. It is caused by the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilum, often associated with the same ticks that transmit Lyme disease. One significant feature of anaplasmosis is its position as a potentially severe but often underreported illness. Symptoms may initially resemble the flu, complicating diagnosing it without proper medical evaluation. Recognizing this disease underscores the need for vigilance and comprehensive monitoring of symptoms after tick exposure. Awareness can not only aid in personal health management but also contribute to broader efforts in preventing spread and informing public health policies.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Geographic Risks
Understanding geographic risks associated with tick-borne diseases is important for communities and individuals alike. Certain regions, particularly rural areas or places with dense wildlife populations, harbor a higher concentration of ticks. This geographical awareness empowers individuals to assess their risk more realistically, enabling them to take necessary precautions when spending time outdoors. Furthermore, recognizing high-risk areas can help municipalities and health organizations in implementing effective public health strategies.
Behavioral Precautions
Behavioral precautions play a vital role in preventing tick bites and subsequent diseases. Simple tasks such as avoiding tall grasses and sticking to well-trodden paths can significantly reduce exposure. Wearing long sleeves and pants can serve as a physical barrier against bites. These actions not only protect individual health but also foster broader community awareness. By sharing knowledge and encouraging preventive measures, the overall incidence of tick-borne diseases can potentially decrease within at-risk populations.
Protective Clothing and Repellents
Investing in protective clothing and using insect repellents are essential strategies for anyone venturing into tick-prone areas. Clothing treated with permethrin can provide an added layer of defense against bites. Insect repellents, such as DEET or picaridin, offer further protection. This combination not only minimizes the risk of bites but can also boost confidence while enjoying outdoor activities. It’s about creating an environment where individuals can appreciate nature without undue concern over tick encounters. Coupling awareness with practical measures enhances public health promotion significantly.
"Awareness of tick-borne diseases is the first step towards effective prevention and treatment."
Through understanding and dissemination of knowledge regarding tick-borne diseases and preventive strategies, individuals become better equipped to manage their interactions with ticks and protect their health effectively.
Enhancing Awareness and Preparedness
The necessity for sharpening awareness and readiness regarding ticks is paramount in our increasingly interconnected world. While much focus might be directed towards immediate actions post-tick discovery, gaining an understanding and preparedness can be just as crucial. Knowledge not only empowers individuals but also contributes to community health at large. Knowing how to recognize ticks, understanding their habitats, and the diseases they might carry prepares you to act swiftly, should an encounter occur.
Like the old saying goes, "An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure." This holds particularly true when dealing with ticks which are carriers of serious diseases. Awareness is the first step toward prevention. By educating the community, we can minimize risks and foster a healthier environment that reduces tick populations significantly.
Community Education Programs
Workshops and Seminars


Workshops and seminars serve as interactive platforms where community members gather to learn about tick identification and prevention. These events bring together experts who share their knowledge, creating a resource-rich environment for participants. One of the main characteristics of workshops is the practical, hands-on approach that allows individuals to practice identification techniques using actual tick specimens.
These programs not only disseminate information but also encourage participation from attendees.
Unique features include:
- Interactive sessions where attendees can ask questions
- Group discussions that facilitate sharing anecdotes and experiences
While not every location may have robustly attended workshops, those that do often see a spike in local awareness. However, reaching the community effectively can sometimes prove challenging due to scheduling conflicts or lack of interest. Still, the benefits often outweigh the disadvantages.
School Involvement
Schools are fertile ground for nurturing young minds, and integrating tick education into curricula can prove to be a powerful strategy. School involvement introduces children to the concept of ticks at a young age, morphed into lessons about ecology and health. This approach fosters awareness not only among students but also extends to families, as children typically relay the information they learn.
The collaborative projects between environmental agencies and schools often culminate in educational fairs or days, broadening the reach of tick education.
Unique features include:
- Curricular materials developed specifically for young learners
- Engagement through art projects or science fairs
Some challenges include ensuring the educators feel confident on the topic. If they lack training, the lesson may inadvertently lead to misinformation. Nevertheless, the overall impact of initiating youth education cannot be overstated and provides long-lasting benefits.
Fact Sheets and Resources
Providing resources such as fact sheets allows anyone curious about ticks to access crucial information easily. These sheets often summarize large swathes of knowledge into bite-sized pieces. Key characteristics often involve clear visuals and succinct bullet points that emphasize ticks’ habitats, how to remove them, and symptoms of tick-borne illnesses.
Such resources can serve as handy reminders for those who fear tick encounters, helping them recognize proper practices whenever they venture outdoors.
Unique features include:
- Visually engaging designs that capture attention
- Easy accessibility at community centers, clinics, and online
The downside? Printed materials can sometimes lead to outdated information unless regularly updated. Digital formats, while more efficient, might not always reach older or less tech-savvy demographics. Nevertheless, having accessible information is a boon for public awareness campaign.
Wildlife Conservation Impact
Healthy Ecosystems
A healthy ecosystem is not just a buzzword; it is vital for maintaining balance in nature, which includes potentially curbing tick populations. Healthy environments tend to harbor natural predators that keep tick numbers in check. Ecosystems filled with diverse flora and fauna create a symphony of relationships which mitigate any one species from overpopulating, including ticks.
The interplay of varying species reduces the circumstances for ticks to thrive. Droughts, habitat destruction, or invasive species can disrupt these intricate networks leading to imbalances that favor pest proliferation.
Unique features include:
- Dependence on biodiversity ensuring resilience against pests
- Cultivation of relative habitats for predator species
Challenges in preserving healthy ecosystems can arise due to human interference and development. Yet regular ecological practices—community-driven conservation efforts—can lead to a win-win situation.
Managing Tick Populations
Efforts toward managing tick populations must involve a meticulous blend of information and action. This involves understanding tick behavior, seasonal activity, and humane eradication efforts. Community-led initiatives can set benchmarks for monitoring tick hotspots, translating direct action into mitigative efforts.
One significant characteristic of tick management includes the allocation of resources for environmental management practices designed to minimize tick habitats through careful land use.
Unique features include:
- Establishing controlled environments through habitat management plans
- Regular community clean-up events to reduce tick breeding grounds
On the flip side, managing populations must be balanced against ecological conservation. Local ecosystems boast invaluable traits, and drastic measures might inadvertently disturb them.
Balancing Biodiversity and Human Interaction
Achieving harmony between biodiversity and human activities is no small feat, especially in areas where people frequent tick-prone habitats. Striking a balance means actively engaging communities to cultivate an understanding of the integral roles that local wildlife play—ticks included.
Education campaigns that promote safe recreation practices—like sticking to trails—are essential. They highlight why certain behaviors, like leaving wild areas undisturbed, can deter ticks while allowing wildlife to function naturally within their environment.
Unique features include:
- Information on how human activity directly affects tick populations
- Educational workshops aimed at promoting wildlife safety
Challenges may arise with resistance to change in lifestyle habits, especially among individuals who enjoy recreational activities in tick-infested areas. Nonetheless, bringing awareness of the necessity of coexistence can lead to sustainable practices.
Creating a well-informed community ensures everyone knows how to thrive alongside nature, thus fortifying individual and collective preparedness in mitigating tick encounters.



