Lake Tahoe Fish Species: An In-Depth Guide to Diversity
Intro
Lake Tahoe, nestled in the Sierra Nevada mountains, presents a captivating tableau of natural beauty. Its pristine waters are not merely a visual feast, but also a thriving habitat for various fish species. This diverse freshwater ecosystem is home to both native and introduced fish, each contributing significantly to the aquatic life and ecological balance of the region. Over the years, human activities and environmental changes have created a ripple effect on these species, making it imperative to grasp their intricacies and understand what lies beneath the shimmering surface.
In this comprehensive overview, we dive deep into the fish species of Lake Tahoe, shedding light on their habitats, behaviors, and the delicate balance that characterizes this unique ecosystem. Knowing about these fish isn't just an academic exercise; it's vital for anyone who cares about the environment and wishes to engage in conservation.
The narrative unfolds with an analysis of the native species that have adapted to the lake's chilly depths since time immemorial, followed by a discussion of more recent arrivals that have influenced local habitats. Additionally, the focus will extend to the challenges these fish face due to human interventions and changing environmental conditions.
Through this exploration, we hope to enrich your understanding of how Lake Tahoe’s ichthyological tapestry is woven together, fostering not just appreciation but also a sense of responsibility for its preservation.
Prelude to Lake Tahoe
Lake Tahoe not only captivates with its striking natural beauty, but also serves as a critical ecosystem house to a diverse range of fish species. Understanding Lake Tahoe’s complexities—the climate, geography, and historical significance—allows for a more nuanced exploration of its ichthyological diversity. By looking into these aspects, it becomes clear why this area is considered a treasure, not only for its scenery but also for its ecological vitality.
Geographical Overview
Location and Physical Features
Lake Tahoe's location, nestled between the Sierra Nevada mountains, makes it one of the largest alpine lakes in North America. Geographically, it's positioned straddling the borders of California and Nevada, which adds layers of jurisdictional complexity when it comes to resource management. The lake's depth, at over 1,600 feet, is significant, making it clearer and colder than many lakes. This clarity is a double-edged sword; it supports specific plant life, but also poses challenges for introduced species as they adapt to this unique environment. The physical features—rugged shorelines and striking mountain backdrops—offer not just a spectacle, but also crucial habitats reflecting the larger ecosystem interconnections.
Climate and Weather Patterns
The climate around Lake Tahoe varies greatly by season, lending itself to the richness of its biodiversity. Winters are typically long and cold, while summers see warm, sunny days. This fluctuation is essential; it dictates breeding cycles and feeding patterns across different fish species. For instance, the colder months allow for certain species to thrive as they adapt to deeper, more temperate water layers. However, increased tourism during the summer months brings environmental stress, influencing local wildlife behaviors. Understanding these patterns helps in anticipating seasonal changes that can impact fish populations and their habitats.
Hydrology and Watershed
Lake Tahoe’s hydrology is fascinating and critical to its ecology. The watershed surrounding the lake plays a vital role in maintaining its water quality and flow. With over 60 tributaries feeding into the lake, the freshwater system is both a life-source and an environmental challenge. The unique hydrological characteristics—such as minimal inflow but significant outflow through the Truckee River—ensure a delicate balance of nutrients and temperature. However, any pollutants entering the watershed can significantly affect fish habitats, meaning that monitoring this system is essential for sustaining fish populations.
Historical Significance
Indigenous Tribes and Fishing Traditions
For centuries, Indigenous tribes such as the Washoe have harmoniously coexisted with Lake Tahoe, relying on its abundant natural resources for sustenance. Their fishing traditions illustrate a profound understanding of the land and its ecosystems. These tribes weren't just passive observers; they actively engaged in sustainable practices, demonstrating an ancient perspective on conservation that resonates today. Recognizing these traditions gives depth to our understanding of the lake's ecological importance, emphasizing that fishing is not merely an activity but a cultural legacy tied to the land itself.
Development and Environmental Changes
With the arrival of settlers and subsequent development, Lake Tahoe experienced significant environmental changes. Urban expansion and tourism have altered the natural landscape, impacting fish populations considerably. Changes in land use have contributed to habitat loss and pollution, generating new challenges for native species. Studying this evolution provides insight into the effects of human activity on the ecosystem, highlighting the urgent need for balance between development and conservation efforts.
Ichthyological Diversity in Lake Tahoe
The study of fish species in Lake Tahoe unfolds a complex tapestry of ecological dynamics. Understanding ichthyological diversity is crucial, not just for anglers or biologists, but for anyone invested in the health of this unique ecosystem. The diverse fish populations play an important role in maintaining the balance of the aquatic environment, serving as indicators of ecological health and fostering biodiversity, which in turn supports other wildlife.
This section delves into two fundamental categories: native fish species, which are indigenous to the lake’s waters, and introduced fish species, which have been brought in through human activity. Examining these groups provides a clearer picture of how fish populations interact with their surroundings and the overarching impact on Lake Tahoe's aquatic system.
Native Fish Species
Lake Tahoe Native Lahontan Cutthroat Trout
One of the crown jewels of Lake Tahoe’s fish species is the Lahontan Cutthroat Trout, renowned for its striking coloration and historical significance. This trout is not just a fish; it's a symbol of the lake's pristine ecosystem and a testament to resilient native species. The Lahontan Cutthroat varies greatly, showcasing a vibrant orange hue on its belly, which contrasts sharply with the blue depths of the lake.
The presence of this trout contributes significantly to the overall health of the lake. It acts as a top predator, controlling populations of smaller fish, and consequently maintaining balanced food webs. However, its survival is not without challenges. Unique features such as its adaptation to specific lake conditions make it an important species for ecological study and conservation efforts.
"The Lahontan Cutthroat Trout is emblematic of ecological history and plays a central role in maintaining the health of Lake Tahoe's aquatic ecosystem."
Other Native Fish Species Overview
In addition to the Lahontan Cutthroat, Lake Tahoe is home to several other native fish species that also inherit ecological importance. These include the Merriam's Dace and Sierra Nevada Yellow Legged Frog, among others. Each species adds its own unique characteristics to the aquatic system. For example, Merriam’s Dace contributes to the lower-tier fish population, which is essential for nutrient cycling within the waters.
With the diminishing habitats and increasing human activity, each native species faces its own set of challenges. Studying these species provides insights into their adaptation strategies and how they interact within their habitats, adding depth to the understanding of local biodiversity.
Introduced Fish Species


Impact of Stocking on Ecosystem
The introduction of non-native species, particularly through fish stocking initiatives, has had a profound effect on Lake Tahoe's ecosystem. While aimed at enhancing recreational fishing, these actions often lead to unintended consequences. Non-native species, such as the Mackinaw Trout, could outcompete native species for food and habitat, disrupting the established ecological balance.
These changes bring forth environmental challenges, including the alteration of prey-predator dynamics and habitat degradation. A comprehensive study into how these introduced species interact with the ecosystem is vital for developing effective management strategies. Without careful oversight, the delicate balance that supports Lake Tahoe’s natural beauty could tip toward irreparable ecological harm.
Other Non-Native Species Present
Several other non-native fish species inhabit Lake Tahoe, including Rainbow Trout and Kokanee Salmon. These species, while popular among anglers, often cause stress to the native fish population. Their impact can't be ignored, as they compete directly with native species for resources and habitats.
Unique aspects of these introduced fish include their growth rates and reproductive strategies, which differ from those of native species, leading to further complexity in the ecosystem. Understanding these dynamics is pivotal for fishery management and conservation efforts to ensure the sustainability of Lake Tahoe’s unique ichthyological landscape.
Habitat Analysis
Understanding the habitats within Lake Tahoe is pivotal to comprehending its diverse fish species. Various habitats not only provide shelter and feeding grounds but also affect the behavior and lifecycle of fish. This section will delve into aquatic habitats and environmental influences that shape the ecosystem, giving readers insights into the essential frameworks supporting fish populations.
Aquatic Habitats in Lake Tahoe
Shoreline and Nearshore Environments
The shoreline and nearshore environments are critical for different fish species in Lake Tahoe. These areas are typically more productive due to varying depths, abundant vegetation, and nutrients from terrestrial sources. Young fish and spawning adults often frequent these zones because they provide protection and easier access to food.
Key characteristics of these environments include:
- Ecosystem Support: The rich variety of aquatic plants provides shelter and spawning habitats.
- Nutrient-Rich: Decomposing organic matter from land boosts the food web.
- Temperature Moderation: Shallow waters can warm up faster, creating favorable conditions for breeding.
The unique feature of these environments is the transition from land to water, which supports a myriad of species interactions. However, they are also susceptible to human activities like pollution and development, which can negatively impact the quality of these aquatic habitats.
Open Water and Deepwater Zones
Contrarily, the open water and deepwater zones represent a different type of habitat that is less understood but equally important for Lake Tahoe's fish species. These deeper colder waters contain distinct sets of nutritional resources and provide refuge for various fish species, particularly during warmer months.
Key characteristics include:
- Stable Environment: Lesser temperature fluctuations compared to shallower areas contribute to a stable habitat, critical for certain species.
- Diverse Forage: Larger fish find ample feeding opportunities due to a variety of prey moving through these waters.
A significant feature of these zones is their stratification, where differing layers of water at various depths create unique ecosystems. While advantageous in sustaining fish like the Lahontan cutthroat trout, these areas can experience challenges from climate changes, altering the water quality and affecting the fish populations.
Influence of Environmental Factors
Water Temperature and Quality
Water temperature and quality play crucial roles in the health of Lake Tahoe's fish populations. Various fish species display specific temperature tolerances, which directly influence their distributions throughout the lake. In addition, water quality factors such as dissolved oxygen levels, nutrients, and pollutants can substantially impact these species.
Key characteristics to note include:
- Thermal Stratification: Seasonal temperature layers affect fish behavior and habitat preference.
- Oxygen Levels: Essential for fish survival, variations can lead to stressed populations.
The unique feature of water quality in Lake Tahoe is its relatively pristine nature compared to many other lakes, yet it is not immune to degradation from human activity. This necessitates ongoing monitoring to protect water quality, ensuring a healthy ecosystem for fish.
Interaction of Flora and Fauna
The interaction of flora and fauna is foundational to Lake Tahoe's aquatic ecosystems. Aquatic plants not only provide habitat but also assist in nutrient cycling and water filtration. Fish, in turn, play a crucial role in maintaining plant health by grazing on herbivorous species that may otherwise overtake these environments.
Key characteristics include:
- Biodiversity: High levels of both plant and fish diversity contribute to a resilient ecosystem.
- Mutual Benefits: Healthy plant life supports fish populations while fish species help manage the growth of various flora.
A fascinating feature of this interaction is its cyclical nature, reinforcing the importance of both plants and fish in maintaining balance within Lake Tahoe’s ecosystems. Disruption of this balance can lead to significant ecological consequences, underscoring the necessity of conservation efforts.
Understanding the habitat dynamics of Lake Tahoe is crucial not only for the fish species but for the entire ecological web that this breathtaking lake supports.
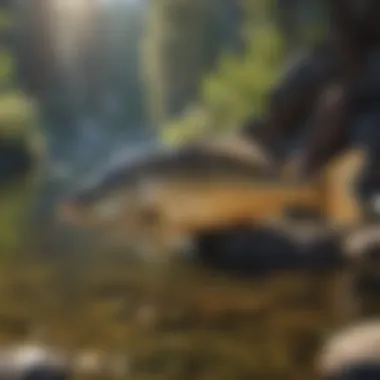

Behavior and Lifecycle of Fish Species
The behavior and lifecycle of fish species in Lake Tahoe are crucial elements that paint a vivid picture of this aquatic habitat. Understanding how these fish interact with their environment, forage for food, and reproduce provides valuable insights into their health and survival, and how these factors interlink with the ecosystem's stability. For professionals in the field of forestry and ecology, grasping these dynamics can illuminate broader patterns of biodiversity and conservation strategies.
Feeding Habits
Predatory vs. Foraging Species
In the realm of Lake Tahoe's fish, there’s a distinct line drawn between predatory and foraging species. Predatory species, like the Lahontan cutthroat trout, showcase noteworthy characteristics that make them stand out—sharp teeth, streamlined bodies, and an inherent instinct to hunt. Their presence is pivotal as they help maintain the population balance among the smaller fish.
On the other hand, foraging species, such as the mountain whitefish, adopt a more passive role in the ecosystem. They primarily feed on zooplankton and insects, contributing to nutrient cycling within the water column. Understanding this distinction enhances comprehension of energy flow within the aquatic system. Predators typically require larger habitats and are linked to specific spawning times of their prey, making habitat quality a focal point of conservation efforts, whereas foragers are often indicators of ecosystem health due to their sensitivity to water quality changes.
Seasonal Variations in Feeding
Seasonal variations in feeding are another critical component to comprehend, as fish adapt their diets based on environmental changes. During the warmer months, the availability of certain prey species peaks, leading predatory fish to exhibit increased feeding activity. Conversely, during colder periods, they may enter a state of reduced metabolism, relying less on food intake.
This adaptability showcases the resilience of fish populations but also highlights their vulnerability to climate shifts. For instance, the shorter food availability due to rising water temperatures may impact growth rates and reproductive success. Understanding these seasonal behaviors allows for improved management practices tailored to maintain the fish population's balance and health throughout varying conditions.
Reproductive Patterns
Spawning Habitats and Timing
Spawning habits and timing are essential topics when discussing the lifecycle of fish species in Lake Tahoe. Spawning typically occurs in specific habitats that provide shelter and protection for eggs, with rocky shorelines and shallow waters being preferred spots. For instance, the Lahontan cutthroat trout often chooses gravel beds where water currents help oxygenate the eggs.
These habitats exhibit unique features that assure not only the survival of the young but also the continuation of the species. The timing of spawning is influenced by various factors, including water temperatures and moon phases, aligning with their natural cycles, thus enhancing the odds of successful reproduction.
Juvenile Development Stages
The juvenile development stages of fish are equally significant in this discourse. After hatching, juvenile fish transition through various stages of growth, classified from larval forms to more developed fry stages. This period is critical for survival, as young fish are often preyed upon by larger species and require specific environmental conditions to thrive.
It’s essential during this stage to understand that juvenile fish often seek distinct habitats that differ from adults. For example, young fish might congregate in shallow waters where they can find both protection from predators and an abundance of food. Recognizing these stages and the associated habitats helps conservationists and researchers devise strategies to protect vulnerable populations effectively.
"The complexities of feeding and reproductive behaviors are not just intriguing; they are fundamental for creating effective conservation strategies for Lake Tahoe’s diverse fish species."
Conservation Challenges
Conservation challenges in Lake Tahoe present vital discussions on the health and sustainability of its aquatic ecosystems. The unique ecology of this region is under threat from multiple fronts, including pollution and human activities. Understanding the intertwining facets of these challenges highlights the urgency of conservation efforts and the strategies necessary to mitigate adverse impacts.
Human Impact
Pollution and Water Management
Pollution in Lake Tahoe is a serious concern that affects water quality and fish populations. Sources of contamination can range from urban runoff to septic systems. A critical aspect of pollution in this region is how it affects the clarity and health of the waters which are essential for aquatic life.
One of the significant features of water management initiatives has been the implementation of stricter regulations and proactive measures for wastewater treatment. This approach not only helps to reduce pollutants entering the lake but also aids in preserving the delicate balance of the ecosystem. Effective water management practices prove to be a beneficial strategy as they can enhance biodiversity by stabilizing habitats for native fish species. However, challenges remain, particularly regarding public compliance and infrastructure limitations, which often slow progress in tackling these issues.
Recreational Activities and Overfishing
Recreational activities like fishing, boating, and swimming draw thousands of visitors each year to the breathtaking shores of Lake Tahoe. While these activities are vital for the local economy, they introduce significant pressures on fish populations through overfishing and habitat disruption.
The key characteristic of recreational activities lies in their dual nature: they can both promote awareness about fisheries and simultaneously threaten fish stocks. It’s crucial to address overfishing as it can lead to dramatic declines in populations, especially among reproductive adults. Unique features of addressing this issue involve implementing catch-and-release programs and research on sustainable fishing practices. Although these programs show promise, the challenge remains in enforcing guidelines and ensuring awareness among both local fishers and tourists alike.
Climate Change and Ecosystem Resilience
Temperature Increases and Habitat Shifts
The impact of climate change on Lake Tahoe is becoming more evident, particularly through temperature increases that challenge the established habitats of its fish species. Fish populations, especially those like the native Lahontan Cutthroat Trout, are sensitive to slight changes in temperature and water quality.
As temperatures rise, shifting habitats force some species to adapt or migrate, while others face the threat of extinction. This aspect of climate change is crucial for understanding how the fish diversity in Lake Tahoe may evolve. The uniqueness of these habitat shifts emphasizes the need for adaptive conservation strategies, which can both safeguard vulnerable populations and promote resilience against further ecological decline.
Management Strategies for Resilience


Addressing climate change necessitates the adoption of management strategies aimed at increasing the resilience of fish species against environmental stressors. These strategies encompass everything from habitat restoration to active monitoring of fish life cycles and health.
The main feature here revolves around creating a dynamic management plan that adjusts as environmental changes unfold, maximizing stability within fish populations while supporting biodiversity initiatives. However, the effectiveness of these strategies depends heavily on a unified approach involving policymakers, local communities, and conservation organizations. This collaborative effort is fundamentally important, as it ensures the commitment towards maintaining the ecological integrity of Lake Tahoe, which is at risk from both climate change and anthropogenic pressures.
The preservation of Lake Tahoe's fisheries hinges on addressing both human intervention and environmental changes to foster a sustainable aquatic environment for future generations.
Future Perspectives
The future of fish species in Lake Tahoe hinges on understanding their dynamics within an ever-changing ecological framework. As we look ahead, it's vital to dissect the layers of ongoing research initiatives and effective strategies for sustainable management. These components not only safeguard the delicate balance of this unique ecosystem but also ensure that future generations can enjoy the richness that Lake Tahoe's waters provide.
Ongoing Research Initiatives
Monitoring Fish Populations
Monitoring fish populations is a critical aspect of aquatic management aimed at safeguarding Lake Tahoe’s exceptional biodiversity. This process helps determine the health and numbers of local species. By keeping watch on population trends, researchers can quickly react to potential declines caused by environmental shifts or human interference. One of the key characteristics of this initiative is its proactive nature—data collected can guide regulations and management practices promptly.
The unique feature of monitoring is the use of technology, which makes it more accurate and efficient. Drones and sonar technology, for instance, allow researchers to map habitats and track species without disturbing their natural behaviors. However, there can be drawbacks too; the cost of these technologies can be high, and the dependence on skilled personnel is significant. Overall, this initiative plays a crucial role in understanding and maintaining Lake Tahoe's aquatic life.
Community Involvement in Conservation
Community involvement represents a vital pillar in the conservation efforts surrounding Lake Tahoe's fish species. Engaging local residents and stakeholders in conservation provides a grassroots approach that often leads to more effective results. One unique characteristic of community involvement is its ability to harness local knowledge and resources. Residents who frequent the lake can offer insights into changes in fish populations or environmental conditions often overlooked by formal studies.
Additionally, educational programs can foster a sense of stewardship among community members, making them invested in the preservation of their local ecosystem. However, while community-driven initiatives can be powerful, they sometimes lack the scientific rigor that professional studies offer, which can hinder overall effectiveness. Nonetheless, this collaboration between the community and scientific institutions presents a blended approach that enriches conservation efforts.
Strategies for Sustainable Management
Legislative Measures
Legislative measures provide the backbone for sustainable management of fish species in Lake Tahoe. Implementing legal frameworks ensures that conservation efforts are not just recommendations but are enforceable. The key characteristic here is the overarching authority these laws impart, which helps regulate fishing, pollution control, and habitat protection. It sets a clear path for managing interactions between human activities and aquatic ecosystems in a delicate balance.
The unique aspect of legislative measures is the collaboration between different stakeholders, including government bodies, conservation organizations, and local communities. This multifaceted approach can lead to better outcomes, as varied interests and insights are taken into account. However, such measures can face challenges in enforcement, especially in areas with heavy recreational use. Overall, these legal frameworks are fundamental to the future of Lake Tahoe's fish species.
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education are indispensable when addressing conservation in Lake Tahoe. Through educational outreach programs, communities can gain a comprehensive understanding of the ecological significance of their local waters and the species within. One key characteristic of these initiatives is their ability to change public perception and behaviors concerning aquatic life. Increased awareness can lead to more responsible recreational practices and foster community support for conservation measures.
Finale
The conclusion serves as a pivotal point in reinforcing the significance of biodiversity, especially within the delicate ecosystem of Lake Tahoe. As we have explored throughout the article, the fish species in this area are not merely inhabitants but integral components that contribute to a balanced and thriving aquatic environment. The interplay between native and introduced species illustrates the importance of understanding these dynamics in fostering a healthy ecosystem.
Summarizing the Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the bedrock of ecological stability.
- A rich variety of species helps maintain resilience against environmental changes.
- It enhances ecological interactions, such as predator-prey relationships and nutrient cycling.
Moreover, Lake Tahoe's unique geographical and hydrological features create specific habitats that support a wide range of fish species. Each species plays a specific role, from controlling algae to providing food for larger animals. Thus, preserving this diversity is crucial not just for the species themselves but for the health of the entire ecosystem.
Integration with Forest Conservation Efforts
The integration of fish species conservation with forest conservation efforts creates a holistic approach to environmental stewardship. By preserving forested areas around Lake Tahoe, we also protect watersheds that are critical for fish habitats. Forests act as natural filters, improving water quality and providing shade that regulates temperature in aquatic ecosystems.
- Key Characteristic: This interlinked approach highlights the mutual benefits for both terrestrial and aquatic life.
- Unique Feature: Collaborations between different conservation groups enhance the effectiveness of these efforts. For instance, initiatives that combine tree-planting with riverbank stabilization can significantly boost fish habitats.
The main advantage here lies in the synergistic effects—when both ecosystems are healthy, it leads to increased biodiversity and better resilience against climate shifts.
Call to Action for Protection
A call to action for protecting Lake Tahoe's fish species amplifies the urgency of conservation initiatives. It serves not only as a reminder of the responsibilities we bear but also encourages proactive engagement from the community.
- Key Characteristic: Raising awareness about local species and their roles fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility among residents and visitors.
- Unique Feature: Educational programs can help bridge the knowledge gap, turning casual visitors into informed advocates for aquatic protection.
However, effective protection strategies require cooperation from various stakeholders, including government agencies, local communities, and conservationists. The main challenge lies in coordinating these efforts effectively—everyone must be on-board for measures to succeed.
"We do not inherit the earth from our ancestors; we borrow it from our children."
In summary, the urgency of protecting the fish species of Lake Tahoe cannot be overstated. Every action taken towards conservation not only preserves species but also safeguards the overall health of the ecosystem. Without our deliberate and concerted efforts, this beautiful ecological haven may face irreversible changes that could diminish its rich biodiversity.



