Enhancing Forest Conservation: The Vital Role of Bear Awareness Training


Management and Preservation of Evergreen Forests
The historical context of American evergreen forests sheds light on the intricate relationship between humans and these vital ecosystems. Native practices and historical land management approaches have shaped the landscape of evergreen forests, influencing their biodiversity, structure, and resilience over time. By examining the historical context of these forests, researchers and conservationists gain valuable insights into sustainable land management and biodiversity conservation.
Research findings on American evergreen forests provide critical information on biodiversity patterns, ecosystem services, and the impacts of human activities on forest health. By synthesizing the latest research studies, stakeholders can identify areas of concern, implement evidence-based conservation strategies, and advocate for sustainable practices that promote the long-term preservation of evergreen landscapes.
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting American evergreen forests serve as a testament to the collaborative initiatives undertaken to safeguard these valuable ecosystems. Conservation organizations, government agencies, and local communities are actively engaged in conservation projects that aim to protect forests, restore degraded habitats, and mitigate human-induced threats. By showcasing success stories and ongoing conservation efforts, this section highlights the dedication and perseverance of those committed to preserving the beauty and biodiversity of American evergreen forests.
Introduction
Bear awareness training plays a vital role in enhancing forest conservation efforts by promoting coexistence between humans and bears. This introductory section sets the foundation for the article, expounding on the significance of understanding bear behavior, mitigating human-bear conflicts, and implementing effective conservation strategies. Bear awareness training not only ensures human safety but also contributes to the preservation of bear populations and their habitats, fostering a harmonious relationship in forest ecosystems.
Defining Bear Awareness Training
Bear awareness training encompasses a comprehensive program that educates individuals on bear behavior, safety precautions, and conservation principles. It equips participants with the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate bear encounters responsibly and sustainably. Through interactive workshops, field exercises, and educational resources, bear awareness training aims to enhance awareness, mitigate risks, and promote respectful coexistence between humans and bears. By defining the core components of bear awareness training, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of bear dynamics and contribute to forest conservation efforts.
Objective of the Article
The primary objective of this article is to elucidate the critical role of bear awareness training in forest conservation. By delving into the intricacies of bear behavior, human-bear interactions, and conservation strategies, this article aims to highlight the significance of proactive training initiatives. Through a detailed exploration of the benefits and challenges associated with bear awareness training, readers will gain insights into how such programs can enhance forest stewardship, promote sustainable practices, and safeguard both human and bear populations in natural habitats.
Overview of Bear Populations in Forests
Forests harbor diverse bear populations worldwide, ranging from grizzly bears to black bears and polar bears. These majestic creatures play integral roles in ecosystem dynamics, influencing seed dispersal, vegetation growth, and overall biodiversity. Understanding the distribution, habitat preferences, and behavioral patterns of bear populations is essential for forest conservation efforts. By examining the ecological significance of bears in forests, this section sheds light on the intricate relationships between bears, their habitats, and human activities, emphasizing the need for informed conservation strategies to protect these iconic species.
Understanding Bear Behavior
Understanding bear behavior is a pivotal component of the broader discourse on forest conservation and bear awareness training. By delving into the intricacies of bear behavior, individuals can gain crucial insights that aid in fostering a harmonious coexistence between humans and bears within forest ecosystems. This section will elucidate the various facets of bear behavior, shedding light on their social structures, feeding habits, foraging patterns, and seasonal behavior variations.
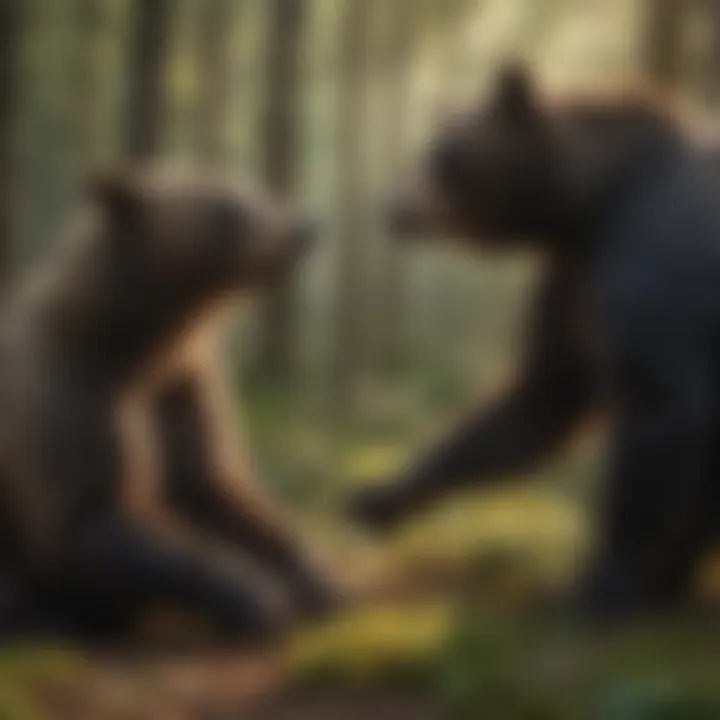


Social Structure and Hierarchies
In the realm of bear societies, the concept of social structure and hierarchies plays a significant role in shaping behavioral dynamics. One key aspect that warrants examination is the Role of Alpha Bears. Alpha bears hold a central position within bear communities, exhibiting distinct behavioral patterns that influence the group's dynamics. Their leadership qualities and dominance impacts intra-group interactions and resource allocation. Understanding the Role of Alpha Bears is integral to comprehending bear social hierarchies and their implications for conservation efforts.
Another critical element of bear behavior is Communication Among Bears. Communication serves as a vital tool for bears to convey information, establish territories, and ensure survival. Bears utilize various vocalizations and body language to communicate within their social groups. Exploring the nuances of Communication Among Bears unveils the sophisticated ways in which these animals interact and cooperate. By understanding communication patterns, conservationists can glean insights into bear behavior and improve conservation strategies.
Feeding Habits and Foraging Patterns
Bears exhibit a diverse range of feeding habits and foraging patterns influenced by their dietary preferences and habitat characteristics. Understanding their feeding habits is essential for assessing their ecological impact on forest ecosystems. Bears play a crucial role as seed dispersers, contributing to plant diversity and ecosystem resilience through their foraging activities. By examining the intricate relationship between bears and their foraging patterns, conservationists can develop strategies to promote healthy ecosystems and bear populations.
Seasonal Behavior Variations
Seasonal behavior variations among bears reflect their adaptation to environmental changes and resource availability throughout the year. Bears undergo distinct behavioral shifts in response to varying seasons, such as hibernation during winter or increased foraging activities in spring and summer. By elucidating these seasonal behavior variations, researchers and conservationists can devise conservation plans that align with bears' natural rhythms. Understanding how seasonal changes influence bear behavior is paramount in implementing effective conservation measures that support sustainable forest management and bear welfare.
Significance of Bear Awareness for Humans
In the context of forest conservation efforts, understanding the significance of bear awareness for humans is paramount. By delving into the intricacies of human-bear interactions, we can mitigate potential conflicts and ensure the safety of both species. Bear awareness training equips individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to coexist harmoniously with these majestic creatures. Through targeted educational initiatives and safety precautions, communities can reduce negative encounters and promote a peaceful cohabitation with bears in forested areas. This section focuses on exploring the critical importance of bear awareness for humans within the broader scope of conservation efforts.
Mitigating Human-Bear Conflicts
Importance of Proper Food Storage
Proper food storage plays a crucial role in mitigating human-bear conflicts. By securely storing food items away from camping sites, individuals can minimize the attraction of bears to human-inhabited areas. Establishing strict protocols for food handling and storage not only protects humans from potential bear encounters but also safeguards the well-being of bear populations. This section delves into the specifics of proper food storage techniques, emphasizing their effectiveness in reducing conflict instances and fostering a safer environment for both humans and bears amidst forest landscapes.
Understanding Camping Guidelines
Understanding camping guidelines is essential for promoting bear awareness among outdoor enthusiasts. By adhering to recommended camping practices such as designated camping areas and waste disposal methods, individuals can actively contribute to minimizing human impacts on bear territories. This subsection sheds light on the significance of following camping guidelines to preserve natural ecosystems and prevent disturbances to bear habitats. Implementing these guidelines not only enhances human safety but also demonstrates a commitment to responsible wilderness stewardship.

Safety Precautions in Bear Country
Bear Spray Usage
Utilizing bear spray is a vital safety precaution in bear country. Bear spray acts as a non-lethal deterrent, providing individuals with a means to deter bear attacks while minimizing harm to the animals. Understanding the proper use and deployment of bear spray enhances personal safety and empowers individuals to respond effectively in bear encounters. This segment explores the benefits of bear spray usage in mitigating risk factors associated with bear encounters and emphasizes its role in promoting coexistence between humans and bears.
Response to Bear Encounters
Responding calmly and appropriately to bear encounters is key to minimizing potential threats and ensuring a safe outcome for both humans and bears. Knowing how to react in various encounter scenarios, such as staying calm, backing away slowly, and avoiding sudden movements, can significantly reduce the likelihood of aggressive bear behavior. This section delves into effective response strategies for bear encounters, highlighting the importance of staying informed and prepared when venturing into bear habitats.
Educational Initiatives for Communities
School Programs
Integrating bear awareness into school programs is instrumental in fostering a culture of respect and understanding towards wildlife. By educating students about bear behavior, conservation practices, and safety measures, schools can instill a sense of responsibility towards wildlife preservation. This subsection explores the benefits of incorporating bear awareness into school curricula, emphasizing the role of education in cultivating a generation of environmentally conscious individuals committed to coexisting harmoniously with nature.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns serve as powerful tools for disseminating crucial information on bear conservation and safety practices to a wider audience. By leveraging various communication channels such as social media, community events, and public outreach programs, these campaigns raise awareness about bear-related issues and promote behavior change among local communities. This segment delves into the effectiveness of public awareness campaigns in advocating for responsible wildlife interactions and fostering a culture of cohabitation between humans and bears.
Conservation Strategies for Bear Habitats
In the realm of forest conservation efforts, the implementation of effective strategies for bear habitats holds paramount importance. Conservation Strategies for Bear Habitats play a crucial role in ensuring the sustainability of bear populations and the preservation of their natural environments. By focusing on specific elements such as habitat restoration projects, corridor conservation efforts, and the mitigation of human-bear conflicts, these strategies aim to foster a balance between human activities and bear habitats.
Preservation of Bear Territories
Habitat Restoration Projects:
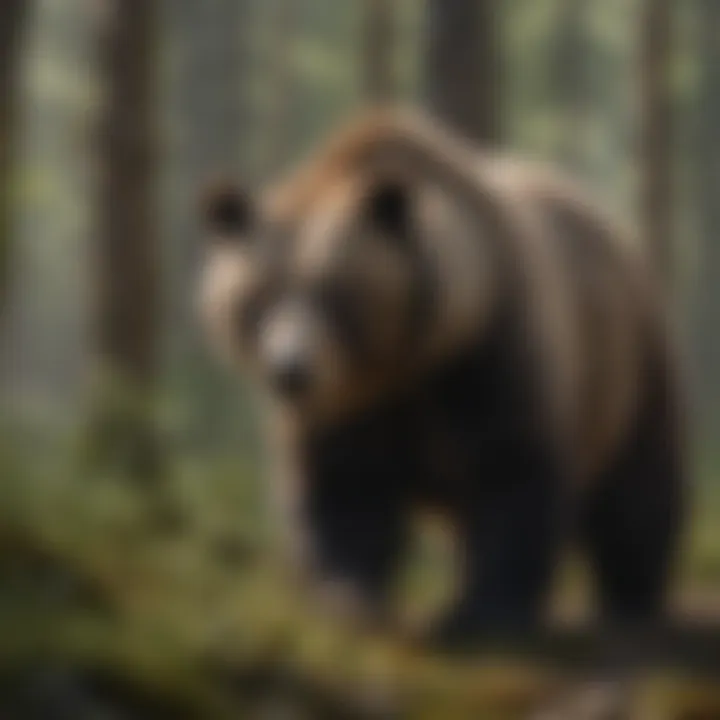


Habitat Restoration Projects encompass a targeted approach towards rejuvenating degraded bear habitats. By restoring essential features such as food sources, shelter, and safe breeding grounds, these projects significantly contribute to the overall well-being of bear populations. One key characteristic of Habitat Restoration Projects is their adaptability to local ecological conditions, ensuring that the restored habitats are suitable for sustaining diverse bear species. This approach is deemed beneficial for this article as it underlines the importance of proactive conservation measures in ensuring the long-term survival of bears. The unique feature of Habitat Restoration Projects lies in their ability to recreate natural ecosystems, providing bears with viable habitats that support their growth and reproduction. While these projects bring substantial benefits to bear populations, challenges such as resource constraints and ecological uncertainties may pose limitations in their execution.
Corridor Conservation Efforts:
Corridor Conservation Efforts focus on establishing interconnected pathways that facilitate the movement of bears between fragmented habitats. By creating corridors that link various bear territories, conservationists aim to enhance genetic diversity and promote species mobility. The key characteristic of Corridor Conservation Efforts lies in their contribution to minimizing the isolation of bear populations, thereby reducing the risks of inbreeding and genetic depletion. This approach is considered a popular choice for this article as it underscores the significance of landscape connectivity in promoting bear conservation. The unique feature of Corridor Conservation Efforts is their role in strengthening ecological resilience by enabling bears to access diverse habitats and resources. While these efforts offer substantial advantages in terms of promoting bear dispersal and adaptation, they may face challenges related to land use conflicts and habitat degradation.
Future Perspectives on Bear Conservation
Future perspectives on bear conservation play a pivotal role in shaping conservation strategies for bear species, ensuring their survival and coexistence with humans in forest environments. This section delves into innovative approaches and anticipates advancements that will guide future conservation efforts. By exploring emerging technologies, traditional knowledge integration, and policy implications, it lays the foundation for sustainable bear management.
Technological Advancements in Bear Monitoring
GPS Tracking Systems
GPS tracking systems revolutionize bear monitoring by providing real-time data on bear movements, territories, and behavior. These systems employ satellite technology to track bears remotely, allowing researchers to gather valuable insights into their habitat use and migration patterns. The key characteristic of GPS tracking systems lies in their precision and effectiveness in monitoring bears across vast forest landscapes. The advantages of GPS tracking systems in this context include enhancing researchers' understanding of bear behavior, facilitating habitat conservation, and mitigating human-bear conflicts. However, challenges such as battery life and signal transmission may impact the continuous tracking of bears.
Camera Traps for Research
Camera traps offer a non-intrusive method for studying bears in their natural habitat, capturing valuable footage and images of these elusive creatures. The key characteristic of camera traps for research is their ability to monitor bears without human interference, providing behavioral insights without disrupting natural behaviors. This technology is a popular choice for conservationists due to its minimal impact on bear populations and its capacity to survey remote or sensitive areas. The unique feature of camera traps lies in their capacity to document a wide range of bear activities, from feeding behaviors to social interactions. While camera traps enhance research capabilities, challenges like weather conditions and camera placement may affect data collection and analysis.
Integration of Traditional Knowledge in Bear Management
The integration of traditional knowledge in bear management acknowledges indigenous communities' deep understanding of bear behaviors, habitats, and conservation practices. This approach combines ancestral wisdom with modern conservation strategies, emphasizing the value of local expertise in promoting sustainable bear conservation. By incorporating traditional practices such as bear ceremonies, storytelling, and land stewardship, communities play a vital role in preserving bear populations and habitats.
Policy Implications and Advocacy
Legislation for Bear Protection
Legislation for bear protection establishes legal frameworks to safeguard bears from threats such as habitat loss, poaching, and human disturbances. The key characteristic of bear protection laws is their role in enforcing conservation measures, regulating human-bear interactions, and preserving bear habitats. This legal framework is a beneficial choice for this article as it underscores the need for stringent protective measures to ensure bear species' long-term survival. The unique feature of bear protection legislation lies in its ability to hold offenders accountable for actions that harm bear populations while promoting coexistence between humans and bears.
Community Engagement in Conservation Policies
Community engagement in conservation policies fosters local support and participation in bear conservation initiatives, creating a sense of ownership and responsibility among residents. The key characteristic of community engagement is its empowerment of communities to collaborate with conservation organizations, government bodies, and researchers in implementing bear-friendly practices. This approach is a popular choice for this article as it emphasizes the importance of community-driven conservation efforts and promotes a grassroots approach to bear conservation. The unique feature of community engagement lies in its ability to bridge communication gaps, build trust, and mobilize collective action for bear protection and habitat preservation.



