Identifying Ticks on Humans: A Comprehensive Guide


Intro
Ticks are small arachnids that can pose significant risks to human health. The ability to identify ticks is crucial, particularly since these parasites can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and anaplasmosis. This guide will provide essential insights into the identification and safe removal of ticks from humans, along with preventive measures. It is important for individuals to understand tick behavior and anatomy to effectively protect themselves from potential infestations.
Tick Anatomy and Behavior
Understanding the anatomy of ticks can enhance identification accuracy. Ticks consist of several parts, including the mouthparts, which can vary significantly between species. These mouthparts aid in their feeding process, positioning ticks either as hard or soft ticks. Hard ticks, in particular, have a shield-like structure on their back, which distinguishes them from their softer counterparts.
Ticks are typically found in wooded areas or tall grasses. They often attach to hosts quickly, so identifying them early is critical. Their life cycle includes various stages: larva, nymph, and adult. Each stage can attach and feed on humans and animals, making knowledge of their life cycle vital.
Common Locations on the Body to Find Ticks
Ticks commonly attach to several areas on the human body. The following locations are where ticks are most often found:
- Behind the ears
- Scalp and hairline
- Underarms
- Behind the knees
- In the groin area
- Between the legs
It is essential to conduct thorough inspections in these areas after spending time outdoors. Some ticks are small and may go unnoticed. Inspecting skin and clothing carefully is necessary for effective tick removal.
Removal Techniques
If you find a tick, prompt removal is necessary to minimize disease transmission risks. Here are the steps for effective tick removal:
- Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible.
- Pull upward with steady, even pressure. Avoid jerking or twisting, as this could leave parts of the tick embedded.
- Clean the area with rubbing alcohol or soap and water after removal.
- Dispose of the tick properly, ideally in a sealed bag or container.
Preventive Measures
To reduce the chances of tick bites, consider these preventive measures:
- Wear light-colored clothing to spot ticks more easily.
- Apply insect repellent containing DEET to exposed skin.
- Stay on trails when hiking and avoid tall grasses and brush.
- Check yourself and pets for ticks after being outdoors.
"Awareness and prevention are key components in avoiding tick bites. Understanding where to find ticks can greatly reduce health risks."
Culmination
This guide provides a streamlined approach to tick identification and removal. Regular inspections and awareness can increase safety when enjoying outdoor activities. By understanding tick behavior, anatomy, and precautionary measures, individuals can better protect themselves from these parasites and the diseases they may transmit.
Prelims to Ticks
Ticks are small arachnids that play a significant role in the transmission of various diseases. As such, they pose a considerable risk to human health, particularly in areas where they are prevalent. Understanding ticks is paramount, as it equips individuals with the knowledge necessary to identify, prevent, and address tick encounters. This article delves into various aspects of ticks, providing essential information that can be beneficial for forestry professionals, academics, and anyone engaged in outdoor activities.
Ticks can be found in diverse environments, often residing in densely vegetated areas, where they wait for a host to pass by. Their ability to attach to humans and animals makes them vectors for diseases like Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and others. Thus, recognizing these pests is not merely academic; it holds practical implications for personal health and safety.
The importance of tick identification is twofold. First, differentiating between tick species can alert one to the specific health risks associated with each. Second, a thorough understanding of tick behavior enhances the capability to perform effective checks after outdoor activities.
In summary, becoming acquainted with ticks is essential for anyone spending time in tick-infested areas. By understanding their biology, habitats, and seasonal behaviors, one can take proactive measures to reduce the risk of tick bites and the subsequent health complications. Awareness of these elements is crucial not just for individual safety but also for public health broadly.
"The first step in tick prevention is knowledge about their existence and behavior. The more informed you are, the safer you can be."
In the sections that follow, we will explore tick biology in greater detail, examine their geographical distribution, and understand why regular tick inspections are necessary.
Biology of Ticks
Understanding the biology of ticks is crucial in identifying them and mitigating the risks associated with their presence. This segment delves into the life cycle of ticks and highlights common species found in America. Recognizing the significance of tick biology can aid in effective prevention strategies and enhance awareness of tick-related health issues.
Life Cycle of Ticks
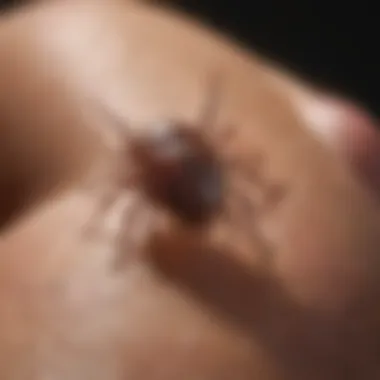

Ticks undergo a complex life cycle consisting of four stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. The entire process can take several months to a few years, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity.
- Eggs: Female ticks lay hundreds to thousands of eggs in the spring or summer. These eggs hatch into larvae after a few weeks.
- Larvae: The six-legged larvae seek out a small host, often from small mammals or birds. They attach to feed on blood for several days. After feeding, they drop off to molt into the next stage.
- Nymphs: Nymphs emerge from larvae and have eight legs. They may also feed on smaller mammals or birds. Nymphs are notorious for transmitting diseases as they feed primarily in the spring and summer.
- Adults: Adult ticks are larger and can feed on a wider range of hosts, including larger mammals like deer or humans. After feeding, adult females lay eggs, thus continuing the cycle.
Understanding this life cycle is essential for identifying the active stages of ticks and the times of year when humans are at greater risk of tick bites.
Common Tick Species in America
Several tick species thrive across various regions in the United States. Here are some of the notable ones:
- Black-legged Tick (Ixodes scapularis): Often known as the deer tick, it is responsible for transmitting Lyme disease. Adults are commonly found from late fall to early spring.
- Western Black-legged Tick (Ixodes pacificus): Similar to the black-legged tick, this species is found on the West Coast, also carrying Lyme disease.
- American Dog Tick (Dermacentor variabilis): Found primarily in the eastern and central United States, it can transmit Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
- Lone Star Tick (Amblyomma americanum): Identified by its distinctive white spot on the back, the lone star tick is prevalent in the southeastern U.S. and can transmit various diseases, including ehrlichiosis.
- Brown Dog Tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus): Commonly found in urban environments, this tick is associated with the transmission of diseases in dogs but can also affect humans.
Understanding the characteristics of these ticks can significantly aid in their identification, promoting awareness of their potential health risks.
Geographical Distribution of Ticks
Understanding the geographical distribution of ticks is crucial to effectively managing tick exposure and preventing tick-borne diseases. This topic not only encompasses where ticks are commonly found but also relates to regional behaviors, climates, and ecosystems that favor tick populations. Specific locations can expose people to variations in tick species and the diseases they carry. Knowing these details informs the public about when and where they’re at risk.
Tick Habitats
Ticks thrive in various environments, often favoring areas with dense vegetation and humidity. Common habitats include:
- Forests: These provide the moisture and cover preferred by ticks. Leaf litter and underbrush are particularly conducive to tick life.
- Tall Grasses: As ticks often wait for hosts at the tips of grass blades, areas with overgrown grasslands present ideal conditions for ticks.
- Woodlands: Shaded and moist, woodlands are exceptional environments where ticks can inhabit without excessive drying.
- Bushy Areas: Places with dense shrubs and undisturbed foliage offer ticks ample spots to attach to passing hosts.
Awareness of these habitats can aid individuals in avoiding high-risk areas, teacing one to be more cautious when venturing into these environments.
Seasonal Tick Activity
Tick activity is influenced predominantly by seasonal changes. Knowledge of this seasonal pattern is paramount for minimizing tick encounters. Generally, ticks are active during warmer months but specific behaviors vary.
- Spring: As temperatures rise, ticks begin to emerge from hibernation. Peak activity often occurs during April and May, particularly in regions where temperatures climb above 45°F (7°C).
- Summer: High activity levels continue, but prevailing heat can cause ticks to retreat to cooler, shaded areas. As people spend more time outdoors, encounters tend to increase significantly.
- Fall: In many areas, tick activity peaks again in late summer to autumn. The drop in temperatures does not eliminate ticks immediately; they remain active until frost.
- Winter: Increased cold can force ticks to become dormant. However, some species, like the black-legged tick, can still be found active on warmer winter days.
By observing these seasonal dynamics, individuals can better plan outdoor activities and take necessary precautions during peak tick activity periods.
Knowing where and when ticks are most active can significantly reduce the risk of exposure and infection.
Why Tick Checks Are Essential
Ticks are small but significant pests that pose serious health risks to humans. Regular tick checks are vital for early detection and to mitigate the risks associated with these parasites. Here, we will explore the specific elements that underscore the necessity of conducting thorough tick checks, the benefits they offer, and important considerations to keep in mind.
Health Risks Associated with Ticks
Ticks are vectors for various diseases, which can have serious health implications. Some of the most notable diseases include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and ehrlichiosis. Understanding these health risks highlights the importance of tick checks. The symptoms of these diseases may not present themselves immediately after a tick bite, making it crucial to perform regular checks, especially after being outdoors in tick habitats.
- Lyme Disease: Caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, Lyme disease is transmitted through the bite of an infected black-legged tick. Early symptoms can resemble flu but can escalate to more serious conditions like arthritis or neurological issues if untreated.
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever: This is a severe tick-borne infection caused by Rickettsia rickettsii. Symptoms often appear suddenly, including fever, headache, and a characteristic rash. The illness can rapidly progress, necessitating prompt medical attention.
- Ehrlichiosis: This disease is transmitted by the lone star tick. Symptoms may include fever, headache, and fatigue. Severe cases can lead to complications involving blood and organ systems.
Consequently, awareness of these health risks can motivate individuals to carry out tick checks regularly.
Identifying Tick-Borne Diseases
Identifying tick-borne diseases involves recognizing the signs and symptoms that may develop after a tick bite. It’s essential to observe your body closely after spending time in areas known for tick activity. Here are some step-by-step guidelines to help in identifying potential illnesses:
- Monitor Symptoms: After a tick bite, watch for any symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, or joint pain. Maintaining a record of these symptoms can help in communicating with healthcare providers.
- Research Common Symptoms: Familiarize yourself with the symptoms specific to prevalent tick-borne diseases. Different diseases present unique symptoms, which can help in quick identification.
- Seek Medical Attention: If any concerning symptoms develop, especially after a tick bite, do not hesitate to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis is critical and can often lead to effective treatment.
"Prevention is better than cure. A simple tick check can go a long way in keeping potential health threats at bay."
The relationship between ticks and the diseases they carry stresses the importance of incorporating tick checks into routine health practices. By understanding the diseases associated with ticks and being vigilant about regular inspections, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of exposure to tick-borne health issues.


Common Areas for Tick Attachment
Understanding the common areas for tick attachment on the body is paramount in effectively detecting and removing these parasites. Ticks tend to favor certain locations where they can easily latch on and remain unnoticed for extended periods. By familiarizing oneself with these areas, individuals can perform more thorough tick checks after potential exposure.
Ticks can attain a secure attachment in various regions. Some of these areas are especially easy to overlook, increasing the likelihood of an undetected tick bite. Awareness of these specific sites not only aids in prompt removal of ticks but also helps in minimizing health risks associated with tick-borne diseases. Attention to the following areas significantly contributes to effective prevention and early detection efforts.
Hair and Scalp
The hair and scalp are particularly appealing habitats for ticks. Ticks search for dark, sheltered areas, which hair provides abundantly. A few key tips to consider include:
- Thorough Checking: When inspecting this area, carefully part the hair and examine the scalp beneath. Look for both ticks and signs of irritation.
- Use of Mirrors: Utilize mirrors to assist in identifying hard-to-see areas. This helps maximize the effectiveness of the check.
Behind the Ears
Ticks can often be found behind the ears, a location often neglected during personal checks. This area is easily accessible yet can be overlooked. Regular examination of behind the ears should be part of any tick-check routine. It's crucial since undetected ticks may lead to increased health risks.
Under the Arms
Underarms present a warm, moist environment that can attract ticks. This area is often less visible, making it necessary for individuals to regularly inspect it during tick checks. Some pointers are:
- Lift the arms: Raise both arms to effectively check the entire area.
- Feel for bumps: Gently feel for any unusual bumps or raised areas.
Around the Waist
The area around the waist can serve as a strategic attachment point, especially if wearing tight-fitting clothing. This is particularly true for those who participate in outdoor activities. Here’s how to inspect:
- Check waistbands: Be sure to remove or search inside clothing to identify ticks.
- Inspect thoroughly: A detailed inspection is necessary in this region to ensure ticks do not go unnoticed.
Between the Legs
Ticks often choose hidden areas for attachment, making the space between the legs another critical area for inspection. Routine checks can help mitigate potential health risks. Remember to:
- Check thoroughly: Perform a careful inspection of all crevices in this region.
- Use protective barriers: Wearing appropriate clothing can help avoid tick contact during hikes or outdoor activities.
Behind the Knees
Behind the knees is another common site for ticks, especially after walking through grassy or wooded areas. This region provides a sheltered space suitable for their needs. When checking:
- Bend the legs: Flex the knees to expose behind the area effectively.
- Gently probe: Feel for any attached ticks or irritation.
On the Back
Ticks can also attach to the back, a harder to access area for self-checks. Regular inspections, especially on warm summer days or after outdoor activities, can help:
- Use a partner: If possible, ask someone to assist with inspections of the back.
- Utilize mirrors: In the absence of help, mirrors can be a valuable tool for checking.
Remember, the key in identifying ticks early is a systematic and thorough approach wherever they are likely to attach. Awareness, frequent checks, and proper inspection methods can significantly diminish the potential for tick-borne illnesses.
How to Perform a Thorough Tick Check
Conducting a thorough tick check is crucial in preventing tick-borne diseases. Ticks are often small and can easily go unnoticed. An effective tick check can reduce the risk of bites and subsequent infections. Regular inspections should be part of outdoor activities, especially in wooded or grassy areas where ticks are prevalent. Knowing how to properly inspect for ticks not only safeguards individual health but also fosters awareness of their presence in the environment.
Methodology for Tick Inspection
The method for performing a tick check should be systematic. Start by ensuring adequate lighting in the area where the check will occur. This helps in spotting the small ticks, which can sometimes be as tiny as a poppy seed.
- Choose the Right Time: After returning from outdoor activities is the best time for inspections.
- Apparel Consideration: Wear light-colored clothing. This contrast makes it easier to spot ticks against your clothes.
- Body Parts to Inspect:
- Partner Checks: If possible, have a partner assist in checking hard-to-see areas.


- Pay close attention to warm, hidden areas of the body. Ticks often prefer these locations.
- Inspect the scalp, behind the ears, under the arms, around the waist, and in between the legs.
- Use both visual checks and hand-feeling to ensure a more comprehensive inspection.
This detailed approach to inspection significantly improves the chances of identifying ticks before they can attach.
Tools for Tick Removal
If a tick is found, having the right tools for removal is essential to prevent disease transmission. Proper tools allow for safe removal without leaving parts of the tick embedded in the skin, which could lead to infections or complications.
- Tick Removal Tool: A specialized tick removal tool, like a hook or tweezers, can be very effective. These help grasp the tick firmly yet safely.
- Container for Tick Storage: Use a small, sealable container to store the tick after removal. This is important for identification in case of symptoms later on.
- Antiseptic Wipes: These are useful for cleaning the bite area after removal.
Using the right tools ensures a clean removal process and can contribute further to health safety by reducing the risks associated with incorrect removal techniques.
What to Do After Tick Removal
After removing a tick, proper aftercare is necessary.
- Clean the Area: First, wash the area thoroughly with soap and water, or use an antiseptic wipe.
- Monitor for Symptoms: Keep an eye on the bite site for a few weeks. Look for any redness, swelling, or the appearance of a rash.
- Document the Tick: Record when and where the tick was removed. This information may help healthcare providers if symptoms develop later.
- Consult a Physician: If you notice any unusual signs or symptoms, contact a healthcare professional. They may recommend testing, especially if you live in a tick-endemic area.
By taking these steps after removal, individuals can minimize the risk of complications from tick bites and stay informed about their health status.
Preventive Measures Against Ticks
Preventive measures against ticks are crucial in minimizing risk of bites. Understanding how to reduce exposure is vital for safety. The importance lies not only in avoiding bites but also in preventing tick-borne illnesses. Effective prevention involves multiple strategies. Each element plays a role in creating a comprehensive approach to protection.
Appropriate Clothing Choices
Choosing the right clothing can significantly reduce the risk of tick bites. Opt for long-sleeved shirts and long pants. Light-colored clothing allows for easy detection of ticks. This contrast helps in spotting the dark ticks before they attach. Tightly woven fabrics are also more effective. Treat clothing with permethrin, an insect repellent, enhances protection. However, be careful to follow application guidelines. Wearing boots and tucking pant legs into them further protects the skin.
- Key clothing tips:
- Wear long sleeves and pants.
- Choose light-colored fabrics.
- Treat clothes with permethrin.
- Tuck pants into boots.
Repellents and Their Efficacy
Repellents are essential for preventing tick bites. The most effective contain DEET or picaridin. These chemicals create a barrier against ticks. Application should be on exposed skin and clothing.
It is important to reapply after sweating or swimming. Generally, repellent effectiveness lasts for several hours, and users should check product labels. It is also beneficial to remember that not all repellents work equally; some may be less effective for ticks compared to mosquitoes.
Consider this: Always verify the concentration of active ingredients for optimal protection.
Environmental Control Tactics
Maintaining a tick-free environment is another vital part of prevention. Yard work can reduce tick habitats. Mow lawns regularly and clear areas of tall grass and brush. Keeping wood piles dry and away from the yard discourages tick presence.
Moreover, implementing barriers such as gravel or wood chips around residential areas reduces ticks. Additionally, encouraging wildlife to stay away from your property can help, as animals like deer and rodents carrier ticks. Using tick control drugs for pets can also minimize risks of bringing ticks indoors.
- Effective tactics include:
- Mow and maintain the lawn.
- Clear brush and tall grass.
- Keep wood piles dry and distant.
- Use barriers to discourage wildlife.
- Treat pets with tick control products.
Adopting these preventive measures greatly enhances safety against ticks. The combination of appropriate clothing, effective use of repellents, and environmental control creates a robust defense against tick bites.
Epilogue
In closing, the significance of recognizing ticks on humans cannot be overstated. Ticks are not just a nuisance; they are potential carriers of various diseases that pose serious health risks. An understanding of tick behavior, anatomy, and common attachment sites enhances one's ability to perform effective inspections. Through proactive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the chance of tick bites.
Health professionals and forestry practitioners alike must incorporate thorough tick checks into their routine activities. Knowledge about tick identification and removal methods protects not just the individual but also the community at large. Misidentification can lead to delays in addressing tick-borne diseases. Therefore, familiarity with tick appearance, such as size, color, and the particular species prevalent in a region, is essential.
"Regular checks and awareness can significantly lower the risk of tick-borne illness."
Moreover, preventive strategies—such as wearing appropriate clothing and using reliable repellents—serve as first lines of defense. Environmental control tactics also contribute to lowering tick populations in commonly frequented areas.
For professionals, it is crucial to communicate these insights effectively. Engaging educational efforts can save lives and promote a culture of proactive health measures. By applying the knowledge acquired throughout this guide, individuals can take informed steps to shield themselves and others from ticks and their potential hazards. In essence, prioritizing tick awareness assures not only personal safety but also enhanced public health.



