Unveiling the Intricacies of Tree Bark: A Detailed Exploration of Nature's Armor
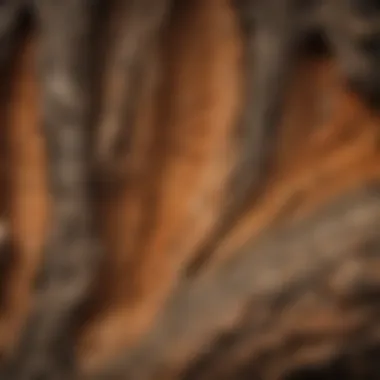

Evergreen Trees Species
Evergreen trees hold a significant place in American forests, showcasing a wide array of species that contribute uniquely to ecosystem dynamics. From the iconic Douglas fir to the majestic redwoods, these trees stand as pillars of resilience and longevity in forested landscapes. Each species boasts distinctive characteristics, ranging from needle-like leaves to cone-bearing structures, painting a diverse tapestry of foliage across the forest canopy.
Delving into the ecological relevance of evergreen trees unveils a world teeming with benefits for biodiversity and environmental stability. These trees play a vital role in oxygen production, carbon sequestration, and habitat provision for wildlife. Their year-round greenery offers a haven for numerous species, fostering a rich tapestry of life within the forest ecosystem.
To ensure the preservation of these invaluable resources, conservation practices are paramount. Implementing measures to safeguard evergreen tree species involves a multi-faceted approach, including protected area designations, reforestation efforts, and sustainable logging practices. Conservationists work tirelessly to maintain the delicate balance of forest ecosystems, recognizing the intrinsic value of evergreens in sustaining ecological health.
Forest Management Techniques
The management of evergreen forests necessitates a comprehensive understanding of wildlife habitat preservation strategies. Sustaining biodiversity and safeguarding critical habitats demand proactive measures such as habitat restoration, buffer zone establishment, and ecological monitoring. By prioritizing wildlife conservation, forest managers contribute to the overarching goal of maintaining a harmonious balance between human activities and natural ecosystems.
In the realm of sustainable logging practices, responsible stewardship is key to ensuring the longevity of forest resources. Sustainable forestry operations adhere to rigorous standards of timber harvesting, focusing on regeneration, minimal impact logging, and ecosystem resilience. By adopting sustainable logging practices, forest managers mitigate the adverse effects of deforestation while promoting a culture of environmental stewardship.
Fire prevention measures stand as a cornerstone of forest management, aiming to avert the catastrophic impact of wildfires on woodland environments. Early detection systems, prescribed burning, and community engagement efforts all play crucial roles in preventing forest fires and protecting forested landscapes. By fostering a culture of fire awareness and preparedness, stakeholders contribute to the preservation of vital forested areas.
Envisioning a future centered on ecosystem restoration calls for ambitious initiatives that seek to revive degraded lands and promote sustainable ecosystems. Ecosystem restoration projects target areas affected by deforestation, pollution, or climate change, with a focus on enhancing biodiversity, soil health, and ecosystem services. Through collaborative efforts and innovative interventions, stakeholders strive to restore balance to disturbed landscapes and secure a resilient future for evergreen forests.
Climate Change Impact on Evergreen Forests
Evaluating the impact of climate change on evergreen forests unveils a complex interplay between ecological systems and environmental pressures. Carbon sequestration emerges as a critical ecosystem service provided by forests, with evergreen trees playing a pivotal role in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. By storing carbon within their biomass and soil, forests contribute significantly to global carbon balance, offsetting anthropogenic emissions and helping combat climate change.
Weather pattern effects present a nuanced dimension of climate change impacts, showcasing shifts in precipitation, temperature, and weather extremes within forested areas. These changes influence forest productivity, species distribution, and ecosystem resilience, underscoring the interconnected nature of climate dynamics and forest health. By closely monitoring weather patterns and adapting management strategies, stakeholders can better equip evergreen forests to withstand the challenges posed by a changing climate.
Biodiversity support within evergreen forests emerges as a critical consideration in the face of climate change. The interconnected web of species within forest ecosystems faces disruptions due to shifting conditions, habitat loss, and invasive species encroachment. Preserving biodiversity hotspots, conserving keystone species, and promoting habitat connectivity become vital actions to safeguard the rich tapestry of life within evergreen forests.
Delving into the localized effects of climate change uncovers region-specific impacts on communities and ecosystems reliant on evergreen forests. From altered growing seasons to increased frequency of extreme weather events, these localized effects present unique challenges that necessitate adaptive measures and community resilience. By understanding the granular impacts of climate change, stakeholders can tailor management strategies to address specific threats and enhance the adaptive capacity of forested landscapes.
Management and Preservation of Evergreen Forests
Tracing the historical context of American evergreen forests unveils a legacy of stewardship, indigenous knowledge, and ecological interconnectedness. Native practices embedded within the cultural tapestry of evergreen landscapes offer insights into sustainable land management, resource utilization, and spiritual connections to the natural world. By honoring this rich heritage and integrating traditional ecological knowledge, modern conservationists harness valuable lessons for preserving the integrity of evergreen forests.
The latest research findings on evergreen forests underscore the dynamic nature of these ecosystems and the pressing need for evidence-based management strategies. Research studies delve into topics such as forest biodiversity, ecosystem resilience, and the impacts of climate change on tree species composition. By synthesizing research outcomes and incorporating scientific knowledge into management practices, stakeholders bolster the adaptive capacity of evergreen forests in the face of ongoing environmental changes.
The conservation efforts dedicated to protecting American evergreen landscapes stand as testaments to human ingenuity, collaboration, and environmental stewardship. Ongoing initiatives focus on land conservation, habitat restoration, community engagement, and policy advocacy, collectively shaping a landscape where evergreen forests thrive and flourish. Success stories within the realm of evergreen forest conservation serve as inspirations for future endeavors, highlighting the potential for positive change when dedicated individuals and organizations unite in a shared vision of ecological sustainability.
Outdoor Activities in Evergreen Forests
Embarking on outdoor adventures within evergreen forests offers a gateway to nature's wonders, from serene hiking trails to secluded camping destinations brimming with rustic charm. Hiking enthusiasts can traverse a tapestry of trails that wind through evergreen canopies, offering glimpses of wildlife, towering trees, and scenic vistas that capture the essence of wilderness exploration.
Discovering top camping spots nestled within American evergreen forests unveils a world of tranquil retreats and off-grid escapades. Camping enthusiasts can immerse themselves in the natural beauty of forested landscapes, serenaded by the rustling of leaves, the call of birds, and the whisper of the wind through towering trees. These camping destinations offer a reprieve from the hustle and bustle of city life, inviting outdoor enthusiasts to reconnect with nature in its purest form.
Nature photography opportunities abound amidst evergreen forests, presenting photographers with enchanting scenes, vibrant flora, and diverse wildlife subjects to capture through their lens. From golden sunsets casting a warm glow on foliage to elusive wildlife sightings amidst the forest underbrush, photographers can hone their craft amid the natural splendor of evergreen landscapes. These photography spots serve as canvases of creativity, inspiring photographers to immortalize the beauty of nature in all its glory.


For birdwatching enthusiasts, evergreen forests stand as prime birding hotspots teeming with avian diversity and natural serenity. Birdwatchers can marvel at the sight of migratory birds, nesting raptors, and forest-dwelling species that call evergreen canopies home. Whether scanning the treetops for elusive songbirds or observing waterfowl by tranquil streams, birdwatching experiences in evergreen forests offer a profound connection to the avian world and the tranquil beauty of forest environments.
Introduction to Tree Bark
Defining Tree Bark
When delving into the exploration of tree bark, the paramount necessity lies in forming a comprehensive understanding of what constitutes tree bark. Defined as the protective outermost layer of a tree, tree bark encompasses a myriad of intricacies that go beyond mere physical appearance to play essential roles in the tree's survival and growth.
Functions of Tree Bark
Protection from External Elements
Protection from External Elements stands as a pivotal function of tree bark, shielding the tree from harsh environmental conditions and potential harm. This function is crucial in ensuring the tree's longevity and well-being amidst external threats, highlighting the resilience and durability inherent in tree bark.
Transport of Nutrients
The Transport of Nutrients mechanism within tree bark facilitates the movement of essential elements and sustenance throughout the tree structure. This vital function ensures the distribution of nutrients from the roots to the branches, fostering growth, strength, and vitality within the tree's system.
Regulation of Water Loss
Regulation of Water Loss is a fundamental function of tree bark that manages the tree's hydration levels. By regulating transpiration and retaining moisture, tree bark plays a pivotal role in preventing dehydration and maintaining optimal water balance essential for the tree's health and survival.
Importance of Tree Bark in Ecosystems
Within the intricate web of ecosystems, the importance of tree bark reverberates far and wide. Tree bark serves as a vital component in ecological systems, contributing to nutrient cycling, habitat provision, and overall biodiversity maintenance.
Anatomy of Tree Bark
Anatomy of Tree Bark is a pivotal focus in this elucidative article on the intricate world of tree bark. Understanding the anatomy of tree bark is crucial in unraveling the complexities and functions of this outer protective layer of trees. By delving into the specific elements and structures that comprise tree bark, readers can grasp the nuances and significance of each layer.
Outer Bark Layers
The outer bark layers, including Cork Cambium and Phelloderm, play a critical role in the protection and transport of nutrients within trees. Cork Cambium, known for its unique properties in insulation and resilience, forms the outermost layer of bark, shielding trees from external elements and providing structural support. On the other hand, Phelloderm, located beneath the cork cambium, aids in nutrient transport and storage, contributing to the overall health and vitality of trees.
Cork Cambium
Cork Cambium, with its characteristic cork cells and suberin deposition, acts as a barrier against moisture loss and protects trees from pathogens and injuries. Its impermeable nature makes it a popular choice for this article as we explore the adaptive features that enable trees to thrive in diverse environments. Despite its advantages in insulation and protection, Cork Cambium may pose challenges in terms of flexibility and growth expansion, impacting the tree's ability to adjust to varying conditions.
Phelloderm
Phelloderm, situated between the cork cambium and phloem, serves as a storage tissue for carbohydrates and facilitates nutrient transport throughout the tree. Its regenerative capabilities and role in wound healing make it a beneficial inclusion in this article on tree bark anatomy. The unique feature of Phelloderm lies in its ability to store energy reserves and support tree growth, underscoring its significance in sustaining the tree's metabolic processes.
Inner Bark Layers
The inner bark layers, comprising Phloem and Vascular Cambium, form the vascular system responsible for nutrient distribution and growth in trees. Phloem, crucial for sugar transport and organic compound transfer, plays a vital role in sustaining tree health and development, making it a focal point of discussion in this article.


Phloem
Phloem, characterized by sieve tubes and companion cells, facilitates the movement of sugars produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the tree. Its efficient transport system and role in maintaining metabolic processes highlight its significance in this comprehensive exploration of tree bark anatomy. Despite its benefits in sugar translocation, Phloem may face challenges related to pathogen attacks and clogging, impacting nutrient distribution within trees.
Vascular Cambium
Vascular Cambium, a meristematic tissue responsible for secondary growth in trees, produces new xylem and phloem cells, enabling trees to increase in girth and volume. Its pivotal role in tree expansion and structural support makes it a pertinent topic in this article on tree bark anatomy. The unique feature of Vascular Cambium lies in its continuous division and differentiation, contributing to the perpetual growth and renewal of tree tissues.
Cambium Layer
The cambium layer, representing the interface between the inner bark and outer bark layers, acts as a zone of cell division and differentiation in trees. Responsible for generating new bark and wood tissues, the cambium layer plays a crucial role in tree growth and regeneration. Its dynamic nature and capacity for tissue renewal align with the overarching theme of adaptation and evolution in tree bark, underscoring its importance in perpetuating tree vitality and resilience.
Types of Tree Bark
Tree bark comes in various forms, each serving specific functions crucial to the trees they adorn. In this comprehensive exploration of tree bark, understanding the different types is vital to grasping the nuanced world of tree anatomy and ecology. Exploring the distinctive characteristics of smooth bark, furrowed bark, and peeling bark sheds light on the adaptability and diversity of trees in different environments.
Smooth Bark
Smooth bark, with its sleek and uniform surface, plays a significant role in protecting trees from external elements like harsh weather conditions and potential predators. Its streamlined appearance provides an aesthetically pleasing look to tree trunks while also serving as a canvas for various biological interactions. Smooth bark acts as a barrier against moisture loss and aids in regulating the tree's internal temperature, showcasing a harmonious blend of functionality and beauty.
Furrowed Bark
Furrowed bark, characterized by deep crevices and ridges, offers a stark contrast to smooth bark varieties. The intricate patterns etched into furrowed bark provide habitats for a diverse range of microorganisms, insects, and even small animals. These crevices act as protective niches, fostering biodiversity within the tree ecosystem. Furrowed bark not only adds texture and visual interest to trees but also enhances their resilience to environmental stressors through increased surface area for nutrient exchange.
Peeling Bark
Peeling bark, known for its shedding outer layers, reflects a dynamic and regenerative aspect of tree growth. This unique bark type allows trees to shed damaged or diseased layers, renewing their protective shield periodically. Peeling bark serves as a visual indicator of a tree's health and growth, revealing the underlying layers that sustain the tree's vitality. Its ability to slough off old bark exposes healthier tissue underneath, facilitating efficient nutrient transport and aiding in the tree's overall health and longevity.
Adaptations and Evolution of Tree Bark
In the comprehensive exploration of tree bark, the section on Adaptations and Evolution holds significant importance as it sheds light on the strategies and changes that tree bark has undergone to survive and thrive in diverse environments. Understanding the evolution of bark adaptations is crucial in deciphering how trees have evolved over time to combat various challenges and threats.
Protective Adaptations
Thick Bark
Thick bark is a pivotal aspect of tree adaptation that plays a crucial role in enhancing the tree's resilience and longevity. Its primary contribution lies in providing a robust outer layer that shields the tree from external factors such as physical damage, fire, and extreme weather conditions. The key characteristic of thick bark is its ability to act as a protective barrier, preventing internal tissues from harm. This makes it a popular choice in the evolutionary process of trees, ensuring their survival in harsh environments.
One unique feature of thick bark is its insulating properties, which help regulate internal temperatures and protect the tree from sudden climatic changes. While thick bark offers exceptional protection, it may pose challenges in nutrient exchange and gas transport due to its density. Despite this, the advantages of thick bark in enhancing tree survival and adaptability make it a valuable asset in the evolutionary journey of tree bark.
Chemical Defenses
Chemical defenses represent another crucial aspect of tree bark adaptations, serving as a proactive mechanism against various threats such as pests, pathogens, and herbivores. The key characteristic of chemical defenses is the production of secondary metabolites that deter or inhibit potential harm to the tree. This defense strategy is a beneficial choice in ensuring tree health and vitality in the face of environmental stressors and attacks.
A unique feature of chemical defenses is their specificity in targeting particular threats, thereby minimizing collateral damage to beneficial organisms or processes within the tree. While chemical defenses offer significant protection, excessive production of defensive compounds may divert resources from growth and reproduction, posing a trade-off in tree survival strategies. Nevertheless, the advantages of chemical defenses in promoting tree resilience highlight its vital role in the evolutionary adaptation of tree bark.


Evolutionary Trends in Bark Characteristics
Evolutionary trends in bark characteristics provide insights into the dynamic nature of tree bark adaptations over geological time scales. By analyzing the changes in bark features across different species and environments, researchers can unravel the underlying patterns in response to evolution-driven selective pressures and ecological shifts.
The descriptions above elucidate the intricate realm of tree bark adaptations and evolution, showcasing the resilience and sophistication of trees in adapting to diverse ecological challenges and evolving landscapes.
Diseases and Threats Affecting Tree Bark
In the comprehensive exploration of tree bark, it is essential to shine a light on the pivotal aspect of Diseases and Threats Affecting Tree Bark. This topic holds substantial significance as it delves into the vulnerabilities that trees face against various ailments and stressors in their environment. By understanding and addressing these threats proactively, we can safeguard the health and longevity of our forest ecosystems. Discussing Diseases and Threats Affecting Tree Bark not only educates us on the challenges trees endure but also underscores the interconnectedness of tree health with the overall ecological balance.
Bark Beetles Infestation
Bark beetles, a formidable foe to trees, are tiny yet destructive insects that infest tree bark, causing widespread damage and sometimes even leading to tree mortality. These insidious pests tunnel through the bark, disrupting the tree's nutrient transport system and weakening its structural integrity. Delving into Bark Beetles Infestation unveils the intricacies of these pests' life cycle, infestation patterns, and the adverse effects they impose on tree health. Understanding the modus operandi of bark beetles is crucial in developing effective management strategies to mitigate their impact and protect tree populations from decimation.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections pose another substantial threat to tree bark, compromising not only the bark's integrity but also the tree's overall health and vitality. These infections can manifest through various symptoms, including discoloration, cankers, and decay, leading to reduced photosynthetic capabilities and structural weakness in trees. Exploring the realm of Fungal Infections sheds light on the diverse array of fungal pathogens that target tree bark and the intricate interactions between fungi and tree defenses. By unraveling the mechanisms of fungal infections, we can bolster our efforts in disease prevention and management, ensuring the resilience of tree populations in the face of fungal threats.
Environmental Stressors Impacting Bark Health
The health of tree bark is intricately intertwined with environmental conditions, making it susceptible to a myriad of stressors that can compromise its vitality. Factors such as pollution, climate change, and habitat alteration can exert detrimental effects on bark health, disrupting its protective functions and leaving trees vulnerable to diseases and infestations. Examining the impact of Environmental Stressors on Bark Health highlights the urgency of mitigating human-induced pressures on tree ecosystems, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices and conservation efforts to preserve the integrity of tree bark and safeguard the well-being of forest environments.
Human Uses of Tree Bark
Historical and Cultural Applications
The historical and cultural significance of tree bark traces back centuries, where different civilizations revered tree bark for its medicinal properties, ceremonial uses, and artistic applications. Various indigenous cultures incorporated tree bark in traditional ceremonies, utilizing its symbolic meaning to connect with nature and spiritual realms. For example, Native American tribes often used bark in their rituals to honor the earth and its resources. In addition, tree bark has been a staple in traditional medicine, with compounds extracted from certain barks used for healing purposes.
Modern Practical Uses
In today's world, tree bark continues to find practical applications across various industries. One of the modern uses of tree bark lies in the production of natural remedies and pharmaceuticals. Extracts from specific barks are incorporated into medicines for their therapeutic properties, showcasing the enduring relevance of tree bark in the medical field. Furthermore, environmentally conscious practices have led to the utilization of tree bark in sustainable packaging materials, aligning with eco-friendly initiatives to reduce waste and promote biodegradability. The versatility of tree bark extends to its usage in landscaping and design, where bark mulch serves both aesthetic and functional purposes in gardens and outdoor spaces.
Overall, the human uses of tree bark span a wide spectrum of historical, cultural, and practical applications, showcasing the enduring importance of this natural resource in various aspects of human life.
Conservation and Management Strategies for Tree Bark
In the realm of tree ecology, the preservation and management of tree bark play a crucial role in ensuring the sustainability of forests and the biodiversity they support. Within the context of this comprehensive exploration of tree bark, the discussion on Conservation and Management Strategies for Tree Bark sheds light on pivotal practices and approaches that aim to protect and nurture this vital component of tree anatomy. By emphasizing the significance of implementing sound management strategies, this section delves into the core principles guiding the conservation of bark integrity and ecological functions within forest ecosystems.
Considering the specific nuances of Conservation and Management Strategies for Tree Bark in this article, it is imperative to highlight the strategic amalgamation of traditional forest management techniques with modern conservation paradigms. By promoting the preservation of old-growth forests and advocating for sustainable bark harvesting practices, forestry professionals and academics can contribute to fostering a balanced approach to bark conservation. The synergy between scientific research, community involvement, and policy frameworks underscores the holistic nature of effective bark management strategies, ensuring the perpetuation of healthy tree populations and thriving ecosystems.
Preservation of Old-Growth Forests
Preserving old-growth forests stands as a cornerstone of Conservation and Management Strategies for Tree Bark. These ancient forests host a diverse array of tree species with centuries-old barks that serve as reservoirs of genetic diversity and ecological resilience. The meticulous preservation of these pristine ecosystems not only safeguards the genetic heritage encapsulated within their bark layers but also nurtures complex symbiotic relationships vital for overall forest health.
The interconnection between old-growth forests and the conservation of tree bark extends beyond mere ecological concerns; it delves into the conservation of cultural and historical legacies embedded in these sacred landscapes. Advocating for the protection of old-growth forests involves recognizing their intrinsic value beyond commercial interests, heralding a paradigm shift towards valuing forests for their irreplaceable contributions to biodiversity conservation and climate regulation.
Sustainable Bark Harvesting Practices
Delving into sustainable bark harvesting practices unveils a nuanced approach to integrating human utilization with environmental preservation. By delineating ethical guidelines and best practices for bark extraction, this facet of Conservation and Management Strategies for Tree Bark encapsulates a harmonious balance between human needs and ecological well-being. Sustainable bark harvesting entails meticulous planning, monitoring, and regulation to ensure that bark resources are replenished in harmony with the natural regeneration processes of trees.
The implementation of sustainable bark harvesting practices not only fosters the longevity of tree populations but also nurtures a sense of stewardship among communities reliant on forest resources. By fostering a symbiotic relationship between human activity and forest ecosystems, sustainable bark harvesting paves the way for a harmonious coexistence that upholds the integrity of tree bark as a vital ecological component. Embracing sustainable practices in bark utilization represents a profound commitment to environmental stewardship and long-term forest sustainability.



